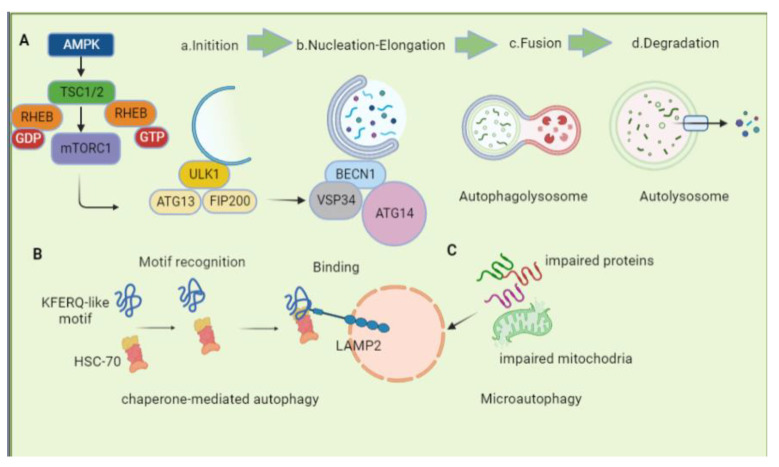
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of different autophagy pathways. (A). macroautophagy: (a) Initiation, the initiation of autophagy is regulated by ULK1-FIP200-ATG13 complex. (b) Nucleation-Elongation, during the phagophore formation, Vps34-BECN1-ATG14 is recruited, and the cytoplasm and organelles are wrapped and devoured; (c) Fusion, fusion and docking of the autophagosome with the lysosome. (d) Degradation, interior autolysosome cargo degradation. (B). Mechanism and regulation of CMA. CMA begins with the recognition of a substrate protein bearing a KFERQ-like motif by HSC70 in the cytosol. In CMA, binding of the HSC70/substrate complex to LAMP2A at the lysosomal membrane causes LAMP2A to multimerize and form a translocation complex, which promotes the internalization of the substrate protein into the lumen for destruction. CMA, chaperone-mediated autophagy; HSC70, Heat shock cognate protein 70 KDa; LAMP-2A, lysosome-associated membrane protein type 2A. (C). Microautophagy: Microautophagy involves the direct uptake of autophagic cargoes by lysosomes, which are then degraded in endolysosomes.