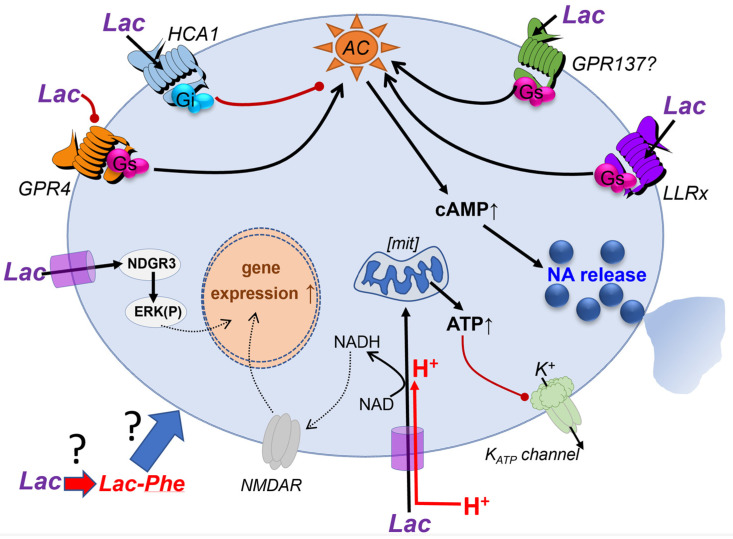
Figure 3.
Summary of putative Lac receptor-mediated signaling mechanisms in brain cells. Lac transported into the cell can be metabolised and/or influence gene expression, e.g., via NMDA receptor modulation or ERK pathway activation. Increased ATP levels may inhibit KATP channel activity and decrease cell excitability. Lac may also act via surface GPCR to stimulate or inhibit neurones. The effects of acidification caused by protons co-imported via MCT require clarification. We also hypothesise that Lac can be converted into Lac-Phe in the brain, the implications of which have yet to be discovered. Black arrows—stimulatory action; red lines—inhibitory. AC—adenylate cyclase; NA—noradrenaline; NDRG3, ERK(P)—phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases; mit—mitochondria. Modified from [48].