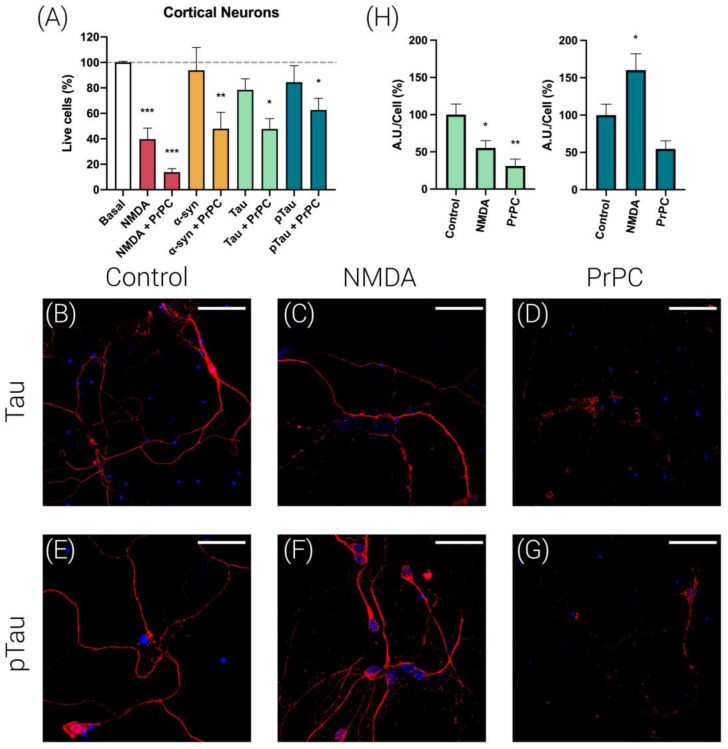
Figure 2.
Cell viability assays and Tau and pTau immunolabeling in primary neurons. (A) Cortical neurons were transfected or not with the cDNA for the human PrPC protein (1 µg) and subsequently treated with NMDA (15 µM, red), alpha-synuclein (4 µM, orange), Tau (1 µM, green) or pTau (1 µM, dark green) for 4 h. For quantification of living cells, cortical neurons were mixed with an equal volume of trypan blue (0.4%). Bar graph shows live cells (colorless cells/total cells × 100, %) in comparison with basal (untreated cells). Values are the mean ± S.E.M. of 5 independent experiments performed in triplicate. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison post hoc test was used for statistical analysis (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 versus basal condition). ANOVA summary: (A) F: 8.70 p < 0.001. Immunocytochemistry assays were performed in hippocampal primary neurons to detect Tau (B–D) and pTau proteins (E–G). Bar graph shows quantification of the amount of fluorescence (Arbitrary Units, A.U.)/cell (%) in comparison with control cells for Tau (green bars) or pTau (dark green bars) (H). Values are the mean ± S.E.M. of 5 independent experiments performed in triplicate. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison post hoc test was used for statistical analysis (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 versus basal condition). ANOVA summary: (H) (left) F: 8.41 p < 0.003. (right) F: 7.88 p < 0.003. Tau protein was detected by an anti-Tau rabbit monoclonal antibody and a secondary Cy3-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (red). pTau protein was detected by an anti-pTau (S396) rabbit monoclonal antibody and a secondary Cy3-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (red). Neurons were treated with NMDA (15 µM) (C,F) or were transfected with the cDNA for the human PrNP (1 µg) (D,G). Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar: 20 µm.