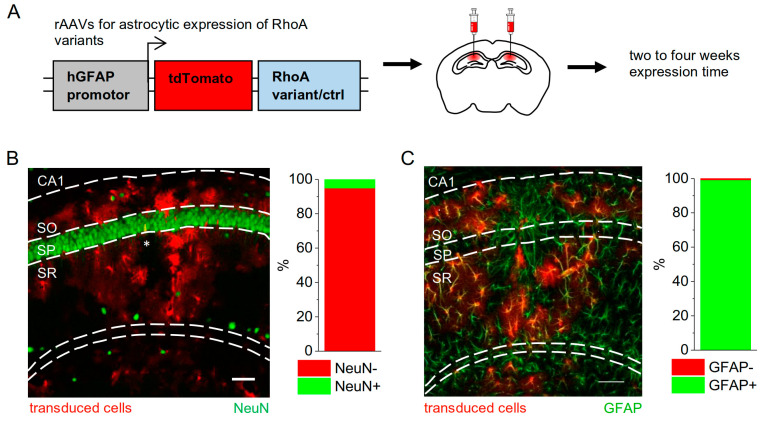
Figure 3.
Strategy and specificity for manipulating astrocytic RhoA activity in vivo. (A) Schematic representation of the recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) design. A human GFAP promotor was used to drive expression of the RhoA variants RhoA-WT/DN/CA fused with tdTomato or only of tdTomato (ctrl). rAAVs were injected into the dorsal hippocampus. Experiments were performed two to four weeks after virus injections. (B) Cellular specificity was tested by visualising transduced cells and neurons using immunohistochemistry. It was found that 94.9 ± 1.9% of the transduced cells were negative for the neuronal marker NeuN (NeuN+, n = 7 tissue slices from 3 animals, 977 cells in total). (C) The vast majority of tdTomato-expressing cells were positive for the astrocyte marker GFAP (99.2 ± 0.18%, n = 9 tissue slices from 3 animals, 2096 cells in total). Scale bars in (B,C) 100 µm. Note that data presented in (B,C) are from independent sets of immunohistochemistry experiments. * in (B) indicates the approximate virus injection site.