Figure 3. Genetic and Phenotypic Heterogeneity in Confirmed ADPKD Cases.
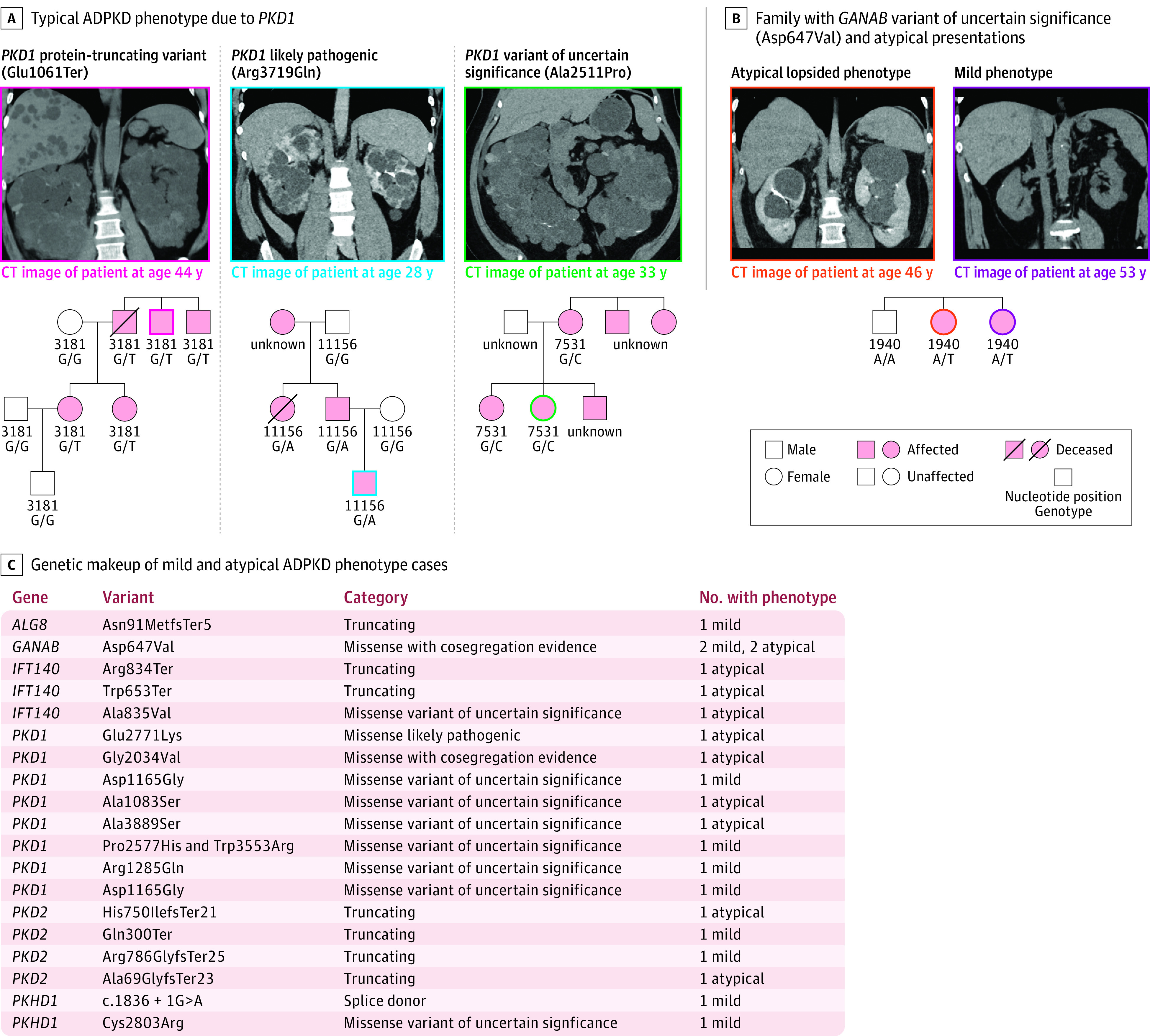
A, Examples: left, a patient with a PKD1 truncating variant (Glu1061Ter) with coronal image in a noncontrast computed tomographic (CT) scan, demonstrating innumerable cortical kidney cysts bilaterally, which enlarge the kidneys and replace the normal kidney parenchyma, consistent with typical ADPKD. Family pedigree shows segregation of ADPKD among members with available genetic and clinical data. Middle, likely pathogenic PKD1 missense variant (Arg3719Gln) carrier in which coronal image from a contrast-enhanced CT scan shows innumerable cortical kidney cysts bilaterally, which enlarge the kidneys and replace the normal kidney parenchyma, consistent with typical ADPKD. Family pedigree shows ADPKD among variant carriers. Right, a carrier of PKD1 (Ala2511Pro), which was been previously classified as likely benign by the Mayo PKD database and variants of uncertain significance by VarSome, in which coronal image from a noncontrast CT scan shows innumerable cortical kidney cysts bilaterally, which enlarge the kidneys and replace the normal kidney parenchyma, consistent with typical ADPKD. In PKD1 or PKD2 variants that were previously unreported or had been classified as benign or variants of uncertain significance, family pedigrees were examined when possible. PKD1 (Ala2511Pro) clearly segregates with ADPKD in pedigree analysis. B, Individuals with atypical or mild ADPKD are much less likely to have a potential variant identified as a contributor to their ADPKD, with only over half of each group being genetically resolved. Among these, few had PKD1 or PKD2 loss of function or likely pathogenic variants, while the majority had novel variants in PKD1, PKD2, or other genes related to cystic kidney disease, including a previously unreported GANAB Asp647Val variant that co-segregates with ADPKD in pedigree analyses. C, Pedigree analysis of 1 family of GANAB (Asp647Val) carriers. The image on the left is a coronal image from a contrast-enhanced CT scan demonstrating relatively mild replacement of kidney parenchyma with a minority of cysts accounting for more than half of the enlarged total kidney volume, consistent with the lopsided subtype of atypical ADPKD.20 The image on the right is a coronal image from a noncontrast CT scan demonstrating relatively few cortical kidney cysts bilaterally with minimal replacement of the normal kidney parenchyma, consistent with mild ADPKD.
