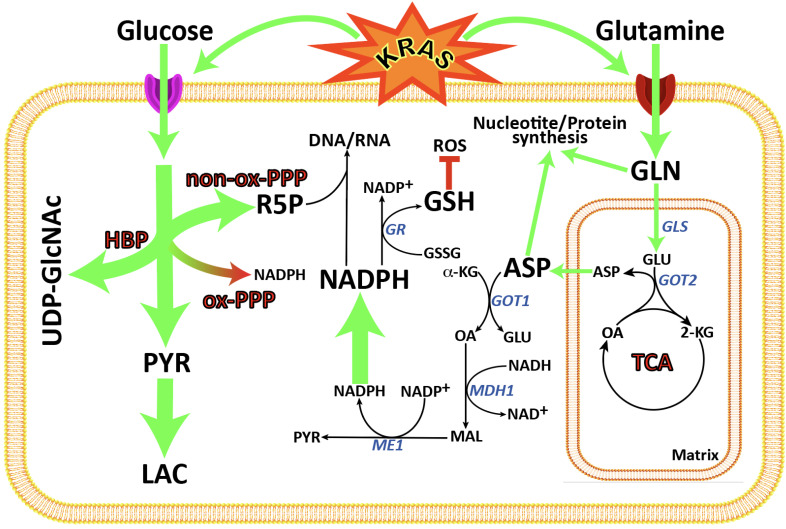
Figure 1.
A synopsis of metabolic pathways rewiring in KRAS-mutant PDAC cell lines. KRAS enhances both glucose and glutamine uptake in PDAC cell lines. Glucose is metabolized merely through aerobic glycolysis to produce intermediates used for pentose phosphate and hexosamine pathways as well as lactate. Glutamine can directly be used for protein and nucleotide synthesis or fluxed into mitochondria where it is converted to aspartate by the action of glutaminase and GOT2. Produced aspartate is transported to the cytosol where it is incorporated into protein or used for synthesis of nonessential amino acids and nucleotides. PDAC cells use aspartate for the generation of NADPH and reduced glutathione by action of GOT1, MDH1, and ME1 to control the redox homeostasis. HBP, hexosamine biosynthetic pathway; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; TCA, Krebs cycle; GLS, glutaminase; GOT1, glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase 1; GOT2, glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase 2; GR, glutathione reductase; MDH1, cytosolic malate dehydrogenase; ME1, cytosolic malic enzyme; α-KG, α-ketogluturate; Asp, aspartate; Glu, glutamate; Gln, glutamine; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; Lac, lactate; Mal, malate; OA, oxaloacetate; Pyr, pyruvate; R5B, ribose-5-phosphate; ROS, reactive oxygen species; UDP-GlcNAc, Uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine.