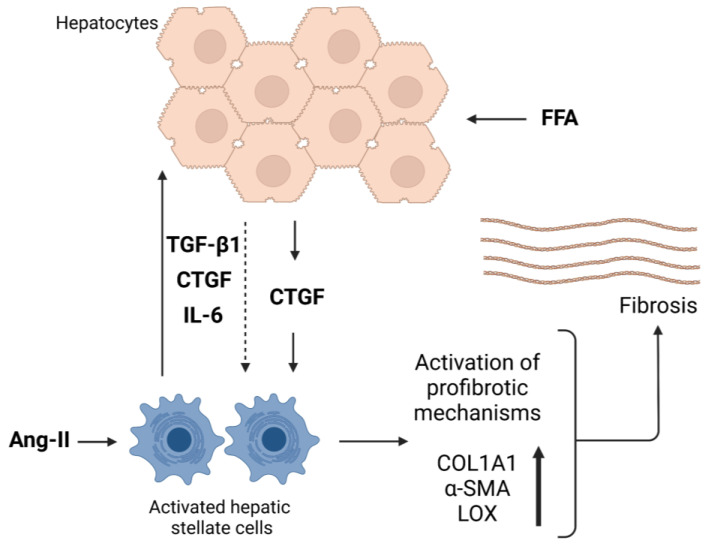
Figure 7.
Proposed schematic overview of CTGF’s function in liver fibrosis in the spheroid model. Under stress conditions, CTGF can be produced by both hepatocytes and activated hepatic stellate cells and can, in addition, itself induce production and release of TGF-β1, IL-6 and CTGF from the co-culture spheroids. Free fatty acids (FFA) create a profibrotic environment, in which co-culture spheroids produce CTGF. Consequently, profibrotic mediators are released from hepatic stellate cells. The profibrotic mechanisms are activated and the production of COL1A1, α-SMA and LOX increases. ECM then accumulates in the spheroids as a final consequence of FFA treatment. Angiotensin II binds to the AT1 receptor on hepatic stellate cells and, through its downstream signaling, induces the production of CTGF and, consequently, other mediators as well. α-SMA—α smooth muscle actin; Ang-II—angiotensin II; COL1A1—collagen, type I, α1; CTGF—connective tissue growth factor; FFA—free fatty acids; IL-6—interleukin 6; LOX—lysyl oxidase; TGF-β1—transforming growth factor beta 1. Created with BioRender.com.