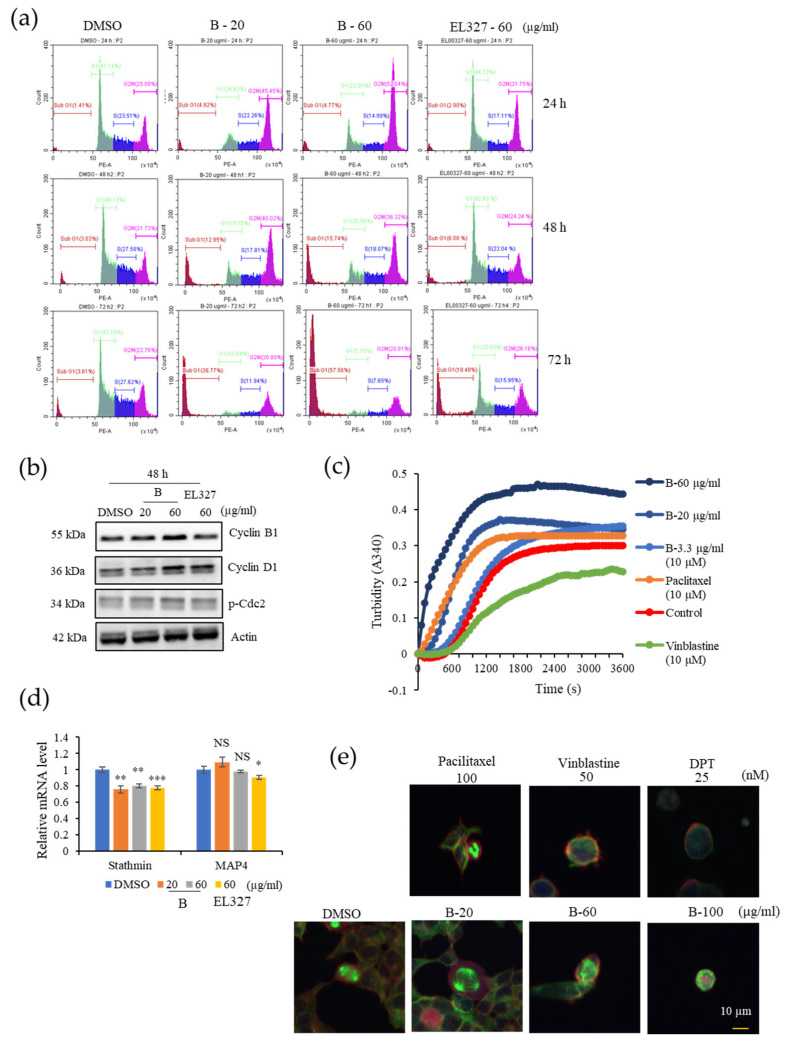
Figure 2.
B induces G2/M phase arrest in Caco2 cells by inducing tubulin polymerization. (a) The cell-cycle distribution of Caco2 cells treated with B (20, 60 µg/mL) or EL000327 (60 µg/mL) for 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h as assessed by flow cytometry. (b) Western blot analysis of cell cycle regulating proteins, Cyclin B1, D1, and p-Cdc2 after treatment with B (20, 60 µg/mL) or EL000327 (60 µg/mL) for 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. (c) Effect of B on tubulin polymerization in vitro, at concentrations of 20, 60, and 3.3 µg/mL. DMSO, paclitaxel, microtubule stabilizer (10 µM), and vinblastine microtubule destabilizer (10 µM) were used as the controls. (d) Relative mRNA levels of stathmin and MAP4, which are associated with microtubule destabilization and stabilization, respectively, after treatment with B (20, 60 µg/mL) or EL000327 (60 µg/mL) for 48 h. (e) Immunofluorescence microscopy of the microtubule organization in the Caco2 cells after treatment with B (20, 60, 100 µg/mL), paclitaxel (100 nM), vinblastine (50 nM) or DPT microtubule destabilizer (25 nM) for 24 h. Actin was stained with Alexa Fluor 568 phalloidin (red), microtubules were stained with α-tubulin antibodies (green), and DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). Results are representative of three independent experiments. Data represent the mean ± S.D. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, NS: no significant difference (p > 0.05) compared with the DMSO-treated control group.