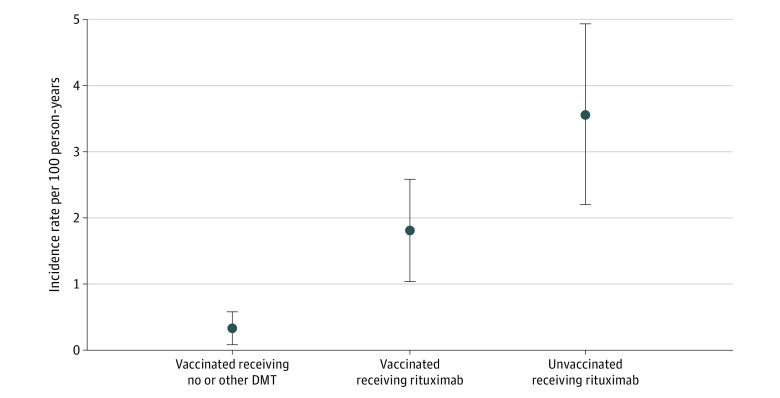
Figure. SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA (mRNA) Vaccination, Rituximab Treatment, and the Incidence of COVID-19 Hospitalizations Among Persons With Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
The figure shows the crude incidence rates of hospitalization for COVID-19 and 95% CIs (error bars) among persons with MS who received 2 doses of mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 who were untreated or treated with disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) that do not interfere with vaccine efficacy (vaccinated receiving no or other DMT, n = 2458), were treated with rituximab and received 2 doses of mRNA vaccines regardless of time since last rituximab infusion (n = 1516), or were treated with rituximab but did not receive any SARS-CoV-2 vaccine doses (n = 437) following the date of first vaccination (December 15, 2020). Individuals in the vaccinated receiving no or other DMT group and the vaccinated receiving rituximab group received mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. The crude incidence of hospitalization is low in all groups yet significantly higher in the vaccinated receiving rituximab group compared with the no or other DMT group and highest among the unvaccinated receiving rituximab group.