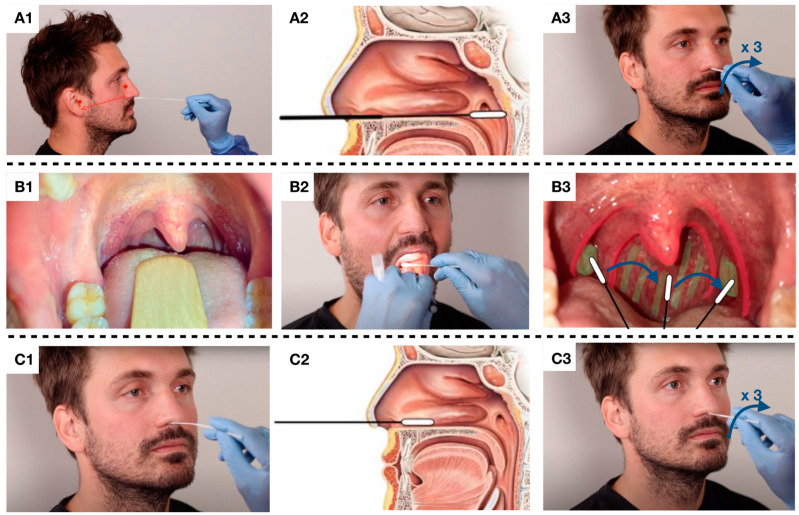
Figure 1.
(A1): The nasopharyngeal swab was performed with the patient’s head tilted slightly back. The swab was inserted into the nasal cavity and pointed towards the earlobe. (A2): The swab was inserted approximately 8–11 cm deep until resistance was met in the form of the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. (A3): The swab was rotated three times and withdrawn. (B1,B2): The oropharyngeal swab was performed using a tongue depressor and head light to improve visualization. (B3): Both palatine tonsils and the posterior oropharyngeal wall was swabbed. (C1,C2): The nasal swab was inserted approximately 1–3 cm into the nasal cavity and brushed along the septum and the inferior nasal concha. (C3): The swab was rotated three times and withdrawn.