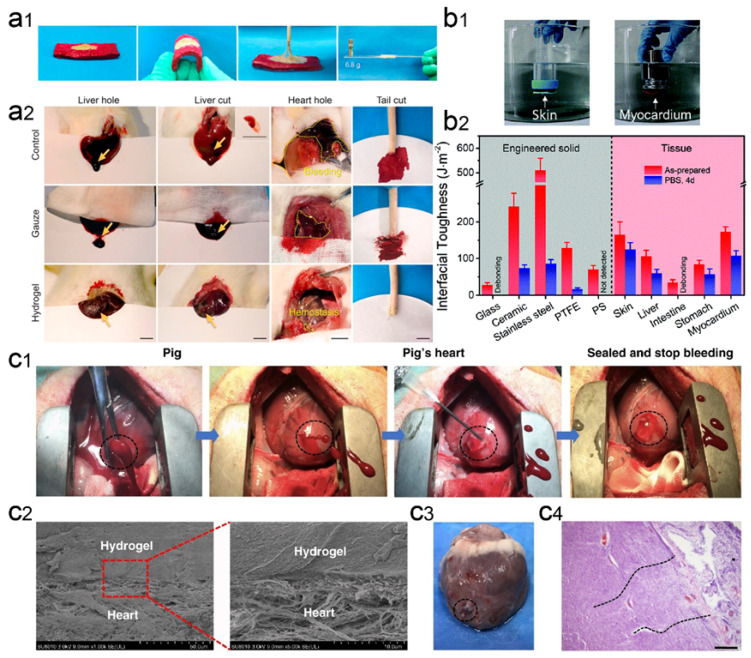
Figure 7.
Wet-adhesive hemostatic hydrogel in heart wounds. (a) Adhesion and hemostatic properties of CS/TA/SF hydrogels. Figure modified from [96] with permission. (a1) The photos show that the hydrogel has strong adhesion to wet pigskin and glass. (a2) Hemostatic images of various untreated wounds covered with gauze or hydrogel. (b) Strong adhesion properties of PCT hydrogels. Figure modified from [97] with permission. (b1) Optical image of direct adhesion of PCT hydrogel between high-density polyethylene substrate and porcine skin or myocardium in PBS environment. (b2) Interfacial toughness of PCT hydrogels with different substrate surfaces before and after 4 days of immersion in PBS. (c) GelMA/HA-NB hydrogel adhesion and hemostatic properties. Figure modified from [98] with permission. (c1) Optical image of rapid hemostatic closure after a heart puncture wound. Blood exudation completely stopped within 10 seconds. (c2) Scanning electron micrographs of the interface between a porcine heart puncture wound and hydrogel. (c3) Autopsy images of the heart were performed after two weeks of postoperative recovery. (c4) Tissue-stained image of the interface between the heart tissue and the matrix gel of a pig heart 2 weeks after postoperative recovery.