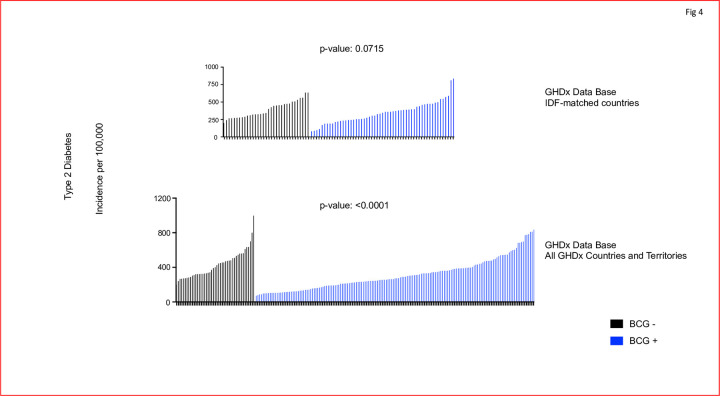
Fig 4. In global population data BCG neonatal vaccinations might confer some protection from T2D onset.
Using IDF-matched countries in the GHDx database, the T2D incidence was not significantly different between countries with (in blue) a childhood BCG program and those without (in black) neonatal BCG vaccinations (p = 0.0715). However, using all the countries and territories available in the GHDx dataset, the T2D incidence was reduced by an average of 28% in those countries with neonatal vaccine programs (p <0.0001). A Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the two groups of countries with and without newborn BCG vaccinations policies. Black lines represent countries without BCG neonatal vaccination programs; blue lines represent countries with BCG vaccination programs. [N = 33 for BCG- countries, N = 55 for BCG+ for the IDF database] [N = 45 for BCG-, N = 159 for BCG+ countries and territories in the GHDx database]. Notation of the countries are in Table 3.