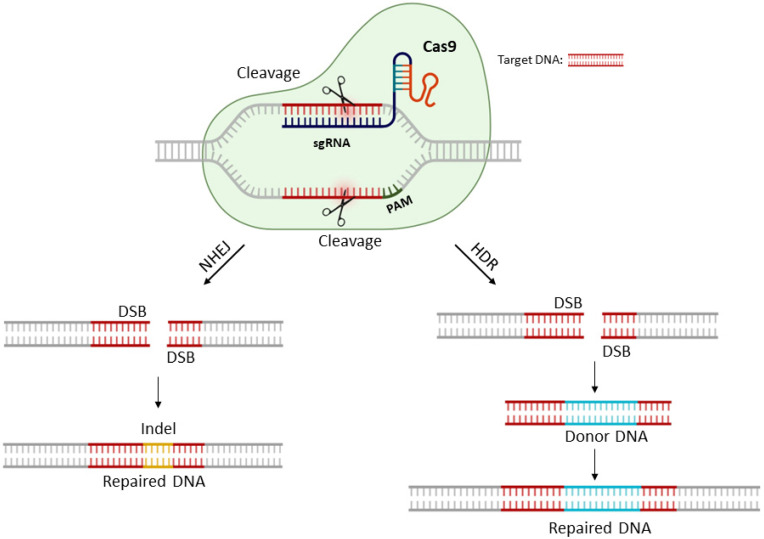
Figure 1.
The CRISPR-Cas9 system mechanism on a target gene. The Cas9 protein is guided by a single-stranded RNA that is complementary to the site of interest, in a specific genomic region. The DNA is cleaved by Cas9, and the occurred DSBs can be repaired by two distinct repair pathways: the error-prone non-homologous ending joining (NHEJ), which will induce indels into the repaired DNA (left) and the homologous dependent repair (HDR) that requires a donor repair template that is incorporated in the target DNA sequence (right).