FIGURE 1.
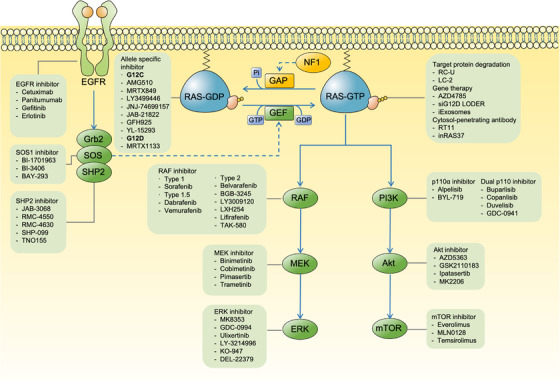
The signal transduction network of RAS and corresponding inhibitors targeting RAS itself and related molecules. External stimuli lead to the activation of RTKs, such as EGFR which in turn activate the SOS, increasing the level of GTP‐bound activated RAS. Blockade of upstream RTKs, SOS and SHP2 potentially down‐regulates the exchange of GDP for GTP in RAS. Inhibitors directly targeting RAS proteins themselves have been developed, such as KRAS G12C allele‐specific inhibitors that lock KRAS in the GDP‐bound inactivated state. Activated RAS orchestrates a large spectrum of biological behaviors of cancers by activating downstream effectors, including RAF‐MEK‐ERK and PI3K‐Akt‐mTOR. Thus, multiple inhibitors have been developed to targeting these cascades at different levels. Abbreviations: RTKs, receptor tyrosine kinase; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; SOS, Son of Sevenless; GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange‐factor; GAP, GTPase‐activating proteins; NF1, neuro‐fibromin 1; SHP2, Src homology‐2 domain‐containing protein tyrosine phosphatase‐2; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3‐kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; Grb2, growth factor receptor‐bound protein 2; RC‐U, (RBD+CRD)CRAF‐U‐Box
