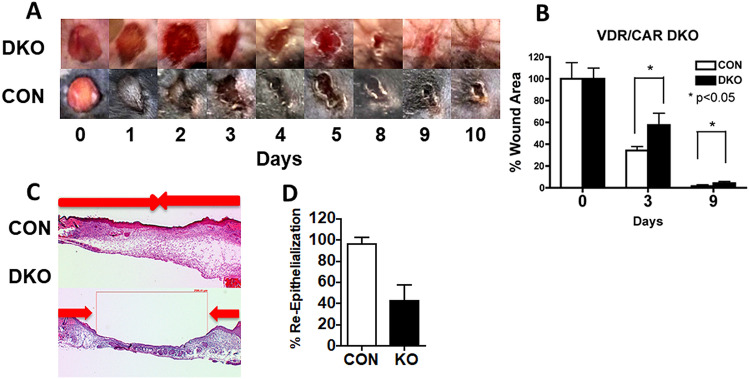
Fig. 1.
Deletion of the vitamin D and calcium receptors delays wound healing. A Six mm full thickness skin biopsies were made on the back of 3 month old DKO mice and their control littermates (CON). The areas of the wounds were measured 0–6 days later and normalized to the original wound area (time 0) in DKO and CON mice. The bars enclose mean ± SD, *p < 0.05 (n = 7–8). B Representative wound photographs in 0–6 days from DKO and CON mice are shown. C Three mm full thickness skin biopsies were made on the back skin of 3 month old DKO and CON, and the re-epithelialization was evaluated histologically at day 3 by H&E staining. Images at higher magnification (boxed) show the edge (white arrows) of epithelial tongues (marked by yellow dotted lines) from which we measured the distance to evaluate the re-epithelialization. D Percent re-epithelialization was quantitatively evaluated by analysis of different cross sections (n = 6, 3 mice each). Percent re-epithelialization was defined as the distance traveled by both epithelial margins (blue arrows) divided by the distance needed to travel to fully re-epithelialize the wound (red bolts). The bars enclose mean ± SD, statistical significance was evaluated by t test *p < 0.05