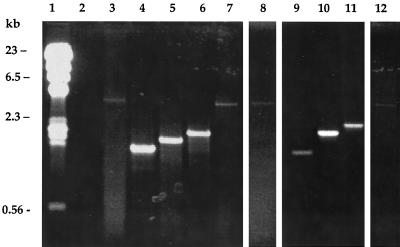
FIG. 3.
PCR amplification of the alpha C protein gene (bca) from bacterial splenic isolates obtained from mice challenged with A909 (lanes 4 to 7) or A909ΔrecA (lanes 9 to 12). DNA was prepared from each isolate by the protoplast method as outlined in Materials and Methods. PCR products were separated on 1% agarose gels. Lane 1, λHindIII markers; lane 2, blank; lane 3, wild-type A909; lanes 4 to 6, individual splenic isolates with alpha C proteins containing one repeat (lane 4), two repeats (lane 5), or three repeats (lane 6); lane 7, isolate not expressing the alpha C protein (null mutant); lane 8, A909ΔrecA; lanes 9 to 11, individual A909ΔrecA splenic isolates with alpha C proteins containing one repeat (lane 9), three repeats (lane 10), or four repeats (lane 11); lane 12, A909ΔrecA-derived isolate not expressing the alpha C protein (null mutant).