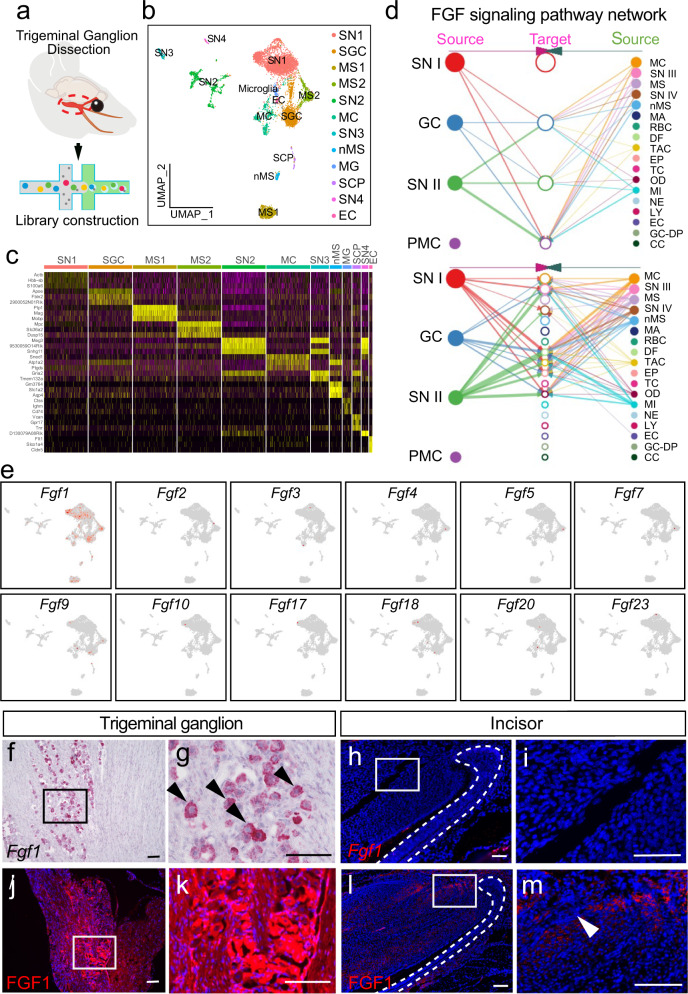
Fig. 2. Sensory neurons secrete FGF1 to regulate mesenchymal cells in the incisor.
a The schematic of the experimental procedure for snRNA-Seq. b 12 clusters across 8679 cells from all cell types in the trigeminal ganglion on a UMAP visualization. SN1–4, sensory neuron type 1–4; SGC, satellite glial cell; MS I–II, myelinating Schwann cell type I-II; nMS non-myelinating Schwann cell; SCP Schwann cell progenitor; MC meningeal cell, EC endothelial cell. c Expression of marker genes of each cell subtype in the mouse trigeminal ganglion. d Hierarchical plot shows the inferred intercellular communication network for FGF signaling. SNI-IV sensory neuron type I–IV, GC glia cell, PMC proximal mesenchymal cell, MC meningeal cell, MS myelinating Schwann cell, nMS non-myelinating Schwann cell, MA macrophage, RBC red blood cell, DF dental follicle cell, TAC TA cell TC T cell, OD odontoblast, MI microglia, NE neutrophil, LY lymphocyte, EC endothelial cell, GC-DP glia cell in dental pulp, CC cycling cell. e Expression levels of canonical FGFs for 12 cell types in the trigeminal ganglion. Fgf1 is highly expressed in sensory neurons, while other FGFs show little expression. f and g The expression of Fgf1 in the trigeminal ganglion. h and i Fgf1 is undetectable in the mesenchyme of the incisor. j and k Protein level of FGF1 in the trigeminal ganglion. l and m Protein level of FGF1 in the incisor. Black arrowheads point to neuron bodies secreting Fgf1; white arrowhead points to FGF1 expression in the incisor. White dotted line outlines the cervical loop. Each experiment was repeated independently three times. Scale bars, 100 μm.