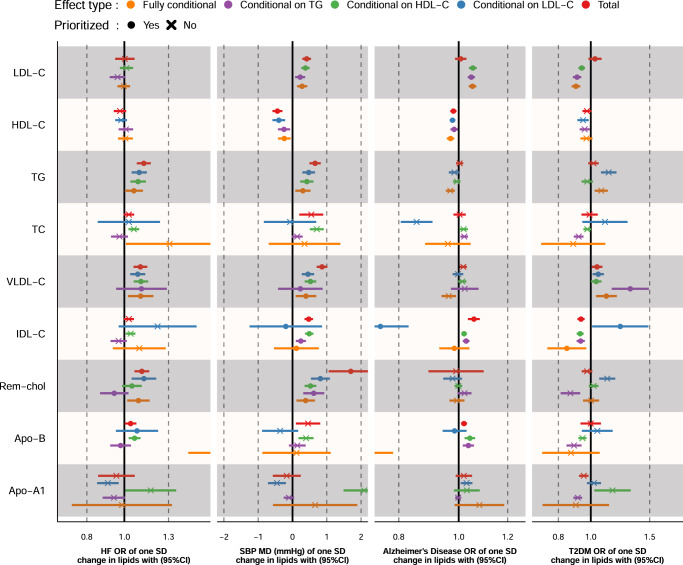
Fig. 5. Mendelian randomization effect estimates of a standard deviation change in cholesterol-containing lipoprotein or apolipoprotein concentration on heart failure (HF), systolic blood pressure (SBP), Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and type 2 diabetes (T2DM).
Prioritized results reflect associations depicted in the causal network of Fig. 3, where 3 out of 5 (or 4 for LDL-C, HDL-C, and TG) estimates were significant at an alpha of 0.05 and directionally concordant. Total: the total lipid effect, Conditional effects either, represent the blood lipid effect of LDL-C, HDL-C or TG singularly, or off all three blood lipids in a single multivariable MR (fully adjusted) model. Fully adjusted models for LDL-C, HDL-C, or TG exposures only conditioned on two of the three blood lipids (e.g., the fully conditional model for LDL-C exposure only conditioned on HDL-C and TG). Analyses were based on a 33,029 subject meta-analysis of Kettunen15 and UCLEB20. Estimates are provided as odds ratio (OR) or mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (95%CI).