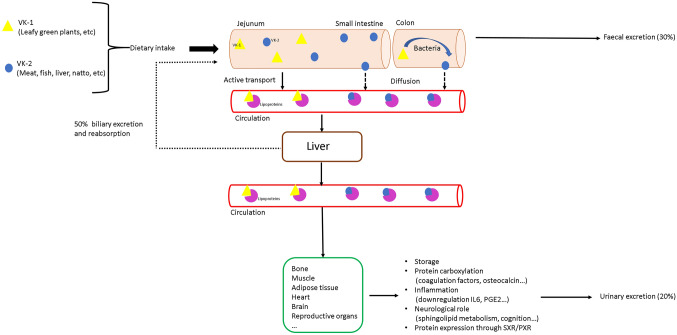
Fig. 2.
Vitamin K uptake and elimination in the body: After oral intake of vitamin K, it is absorbed in the intestine into the thoracic duct and then transported by the bloodstream to the liver (where it undergoes further metabolism and participates in various carboxylation reactions of the blood coagulation factors), adipose tissue (probably for storage), muscles and bones. Approximately 50% of the excretion is reabsorbed, 30% is eliminated via the faeces and approximately 20% via the urine