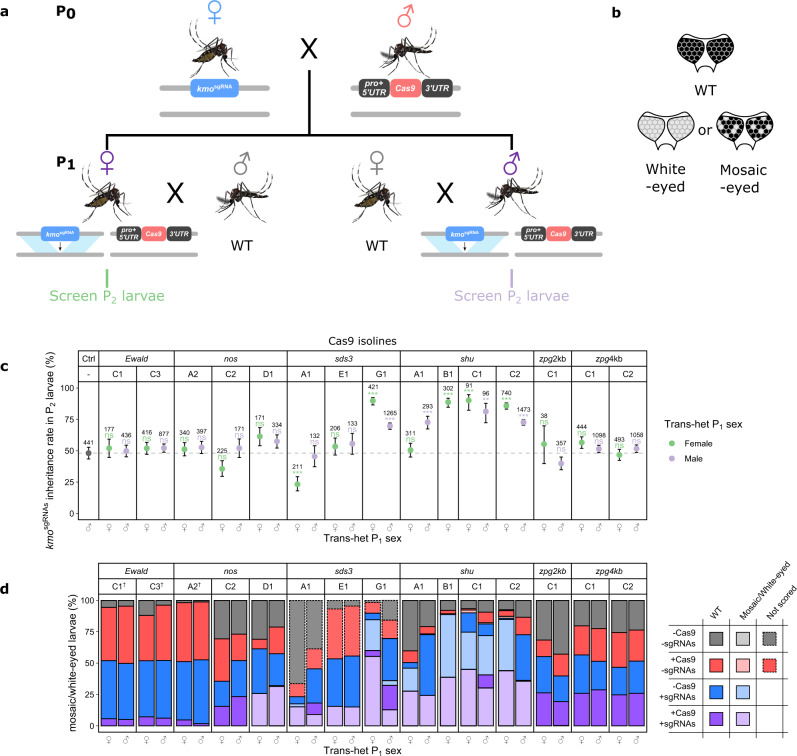
Fig. 1. Cas9 expressed by sds3 and shu regulatory elements causes inheritance bias of the kmosgRNAs element.
a Crossing scheme for determination of Cas9-induced inheritance bias. b Illustration of the difference between WT-, mosaic-, or white-eyed phenotype. c Inheritance rate of the kmosgRNAs in P2 larvae, scored by AmCyan fluorescence. Total number of screened larvae from each cross is presented above corresponding data points. Error bars are the Wilson confidence intervals for the binomial proportion. The confidence intervals are calculated from the pooled progeny count and cannot account for potential over dispersal due to parent by parent ‘batch’ effects. Statistical significance was estimated using Fisher’s two-sided exact test relative to the control inheritance rates represented by the dotted line (p ≥ 0.05ns, p < 0.05*, p < 0.01**, and p < 0.001***). d Percentage of P2 larvae exhibiting WT or mosaic/white-eye phenotype, according to genotype.†The integration sites for EwaldC1-Cas9, EwaldC2-Cas9, and nosA2-Cas9, isolines are likely linked in trans to kmosgRNAs indicated by the low representation of the trans-heterozygote and non-transgenic genotypes in P2. Mosquito figures obtained from Ramirez38,39. Source data are provided as a Source data file. pro = promoter, ♂ = male, ♀ = female.