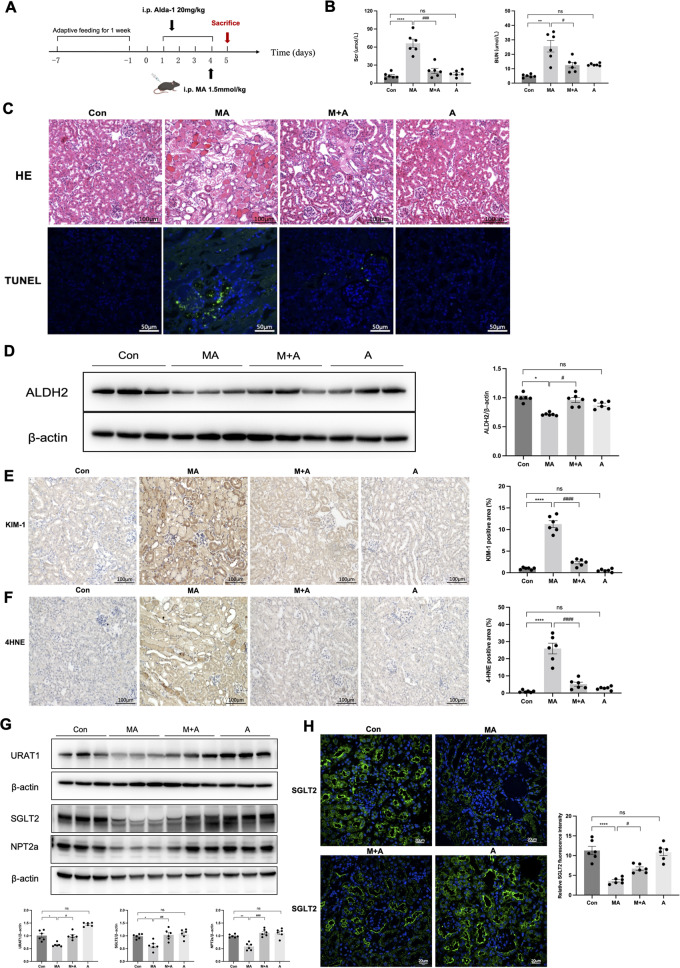
Fig. 3. ALDH2 activation alleviated renal injury in MA-induced AKI.
A Mice were intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected with a single dose of maleic acid (MA) (1.5 mmol/kg) and were sacrificed after 24 h; Alda-1 (ALDH2 agonist, 20 mg/kg) was injected by i.p. for 4 days. B Serum creatinine (Scr) and urea nitrogen (BUN) levels were measured in 4 groups (n = 6). C Images of hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining (n = 6). Scale bars, 100 μm; Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase–mediated dUTP nick end-labelling (TUNEL) assay were used to evaluate the tubular apoptosis (n = 6). Scale bars, 50 μm. D Western blotting and the quantitative analysis of ALDH2 (n = 6). E, F Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of KIM-1 and 4HNE and quantitative analysis (n = 6). G, H The expression of tubular transporter proteins (SGLT2, NPT2a and URAT1) was measured by western blotting (n = 6) and immunofluorescence (n = 6). Scale bars, 20 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, ####P < 0.0001; ns not significant. (Con Control, MA maleic acid, M + A maleic acid + Alda-1, A Alda-1).