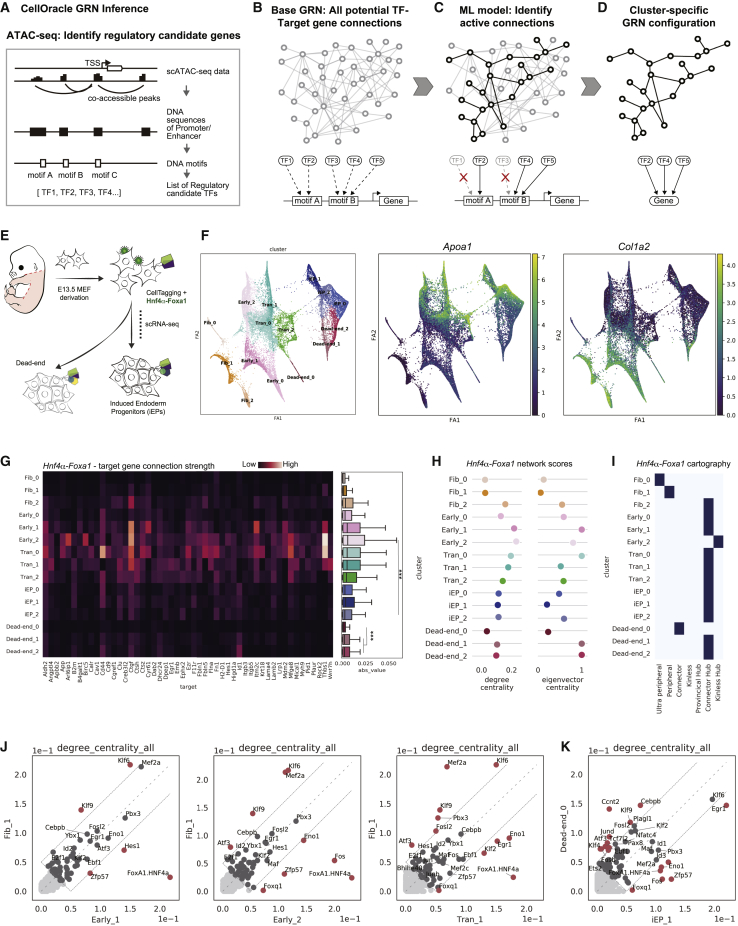
Figure 1.
Application of CellOracle to assess reprogramming GRN dynamics
(A and B) Overview of CellOracle. (A) First, CellOracle uses scATAC-seq data to identify accessible regulatory elements, which are scanned for TF binding motifs, generating a Base GRN—a list of potential regulatory connections between a TF and its target genes (B).
(C) Using single-cell expression data, active connections are identified from all potential connections in the base GRN.
(D) Cell type- and state-specific GRN configurations are constructed by pruning insignificant or weak connections.
(E) Hnf4α and Foxa1-mediated fibroblast to iEP reprogramming.
(F) (Left) Force-directed graph: 15 clusters of cells are grouped into five cell types; fibroblasts (Fib), early transition (Early), transition (Tran), dead-end, and reprogrammed iEPs (iEP). (Right) Projection of Apoa1 (iEP marker) and Col1a2 (fibroblast marker) expression.
(G) CellOracle analysis. Heatmap (left) and boxplot (right) of network edge strength between Hnf4α-Foxa1 and its target genes. ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(H) Degree and eigenvector centrality scores for Hnf4α-Foxa1.
(I) Hnf4α-Foxa1 network cartography terms for each cluster.
(J and K) Scatterplots of degree centrality scores between specific clusters.
(J) Degree centrality score comparison between Fib_1 cluster GRN and other early and transition reprogramming cluster GRNs.
(K) Degree centrality score comparison between iEP_1 and Dead-end_0 cluster GRNs.