Figure 3.
Systematic in silico simulation of TF KO to identify novel regulators of iEP reprogramming
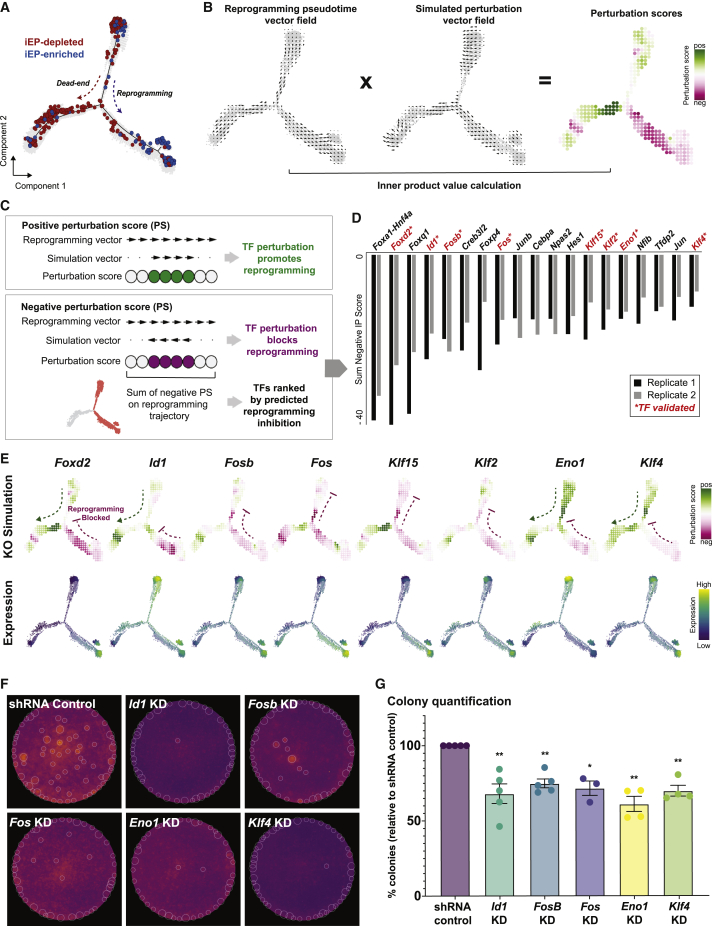
(A) Monocle-based pseudotemporal ordering of 48,515 cells from Biddy et al. (2018), two independent biological replicates.
(B) Schematic for perturbation score calculations. CellOracle calculates a perturbation score by comparing the direction of the simulated cell state transition with the direction of cell differentiation. First, the pseudotime data is summarized by grid points and converted into a 2D gradient vector field. The results of the perturbation simulation are converted into the same vector field format, and the inner product of these vectors is calculated to produce a perturbation score.
(C) A positive perturbation score (green) suggests that the perturbation is predicted to promote reprogramming. In contrast, the negative perturbation score (magenta) represents impaired reprogramming.
(D) Ranked list of TFs based on the sum of the negative perturbation score.
(E) Representative examples of TF KO simulation (top row). Expression of respective genes (bottom row).
(F) Experimental validation of candidate TFs: colony-formation assay.
(G) Colony quantification. n = 5 independent biological replicates for non-targeting scramble shRNA control, Fosb, Id1; n = 4 independent biological replicates for Eno1, Klf4; n = 3 independent biological replicates for Fos; unpaired t test with Welch's correction, two-tailed; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.