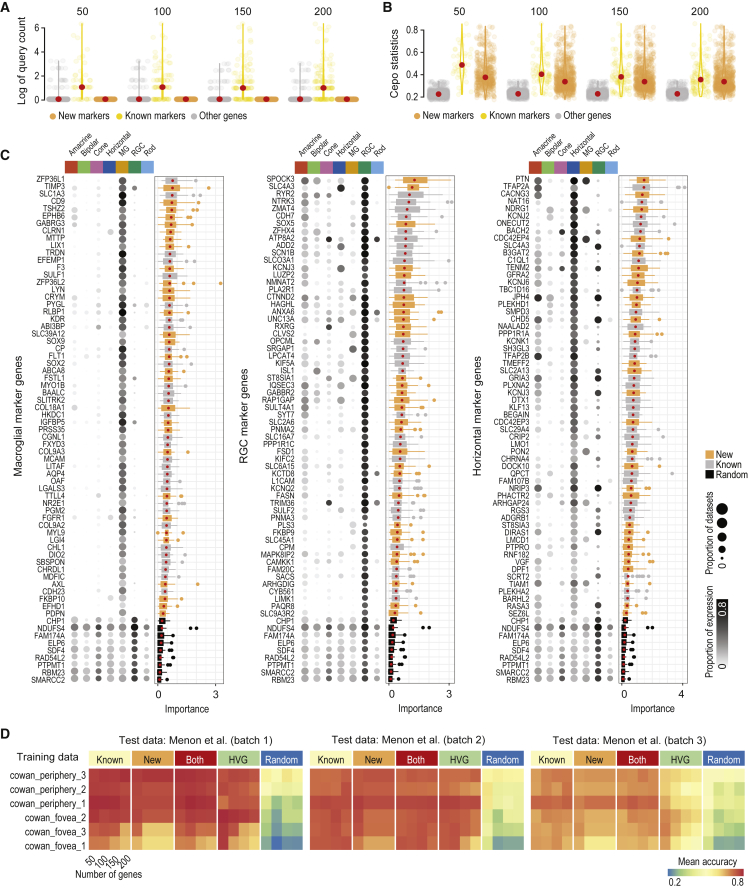
Figure 3.
Identification and validation of novel cell-type-specific gene markers of the retina
(A) Scatter violin plots of log of query count of the top 50, 100, 150, and 200 genes categorized into known or new genes. The scatterplot visualizes the PubMed queries for the results from all cell types and those from non-marker genes for comparison.
(B) Scatter violin plots of the same query results as in (A) but of the respective Cepo statistics.
(C) Cell-type-specific gene markers identified by Cepo. Proportion of cells expressing each marker in each cell type is represented by the gradient color and the proportion of datasets having each marker expressed is represented by the size of the balloons. Importance scores of gene markers are derived from random forest classification of cells using these markers. Novel markers are highlighted in orange and known markers are in gray. Randomly selected genes (in black) are included as controls.
(D) Classification accuracy of independent test data (Menon et al., 2019) from kNN classifiers trained on each of the Cowan datasets using known or new gene markers or their combination, highly variable genes (HVG), and randomly selected genes.