Figure 1.
The chloroplast protein import machineries.
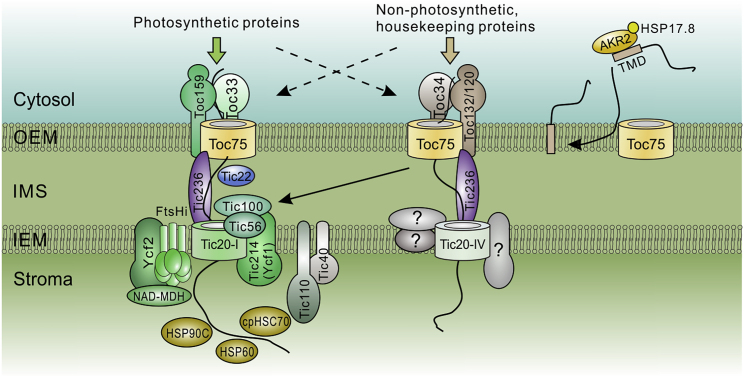
Most nucleus-encoded chloroplast proteins (chloroproteins) are imported into chloroplasts through the OEM-localized TOC and IEM-localized TIC complexes. The core TOC complex comprises Toc159 and Toc34 transit peptide receptors and the channel-forming Toc75. The receptors are GTPases, providing energy at the early stage of import by hydrolyzing GTP. In Arabidopsis (and other plants), the receptors have multiple isoforms. The Toc159 family member Toc159 and the Toc34 family member Toc33-containing TOC complex is mainly in charge of importing highly abundant photosynthetic proteins. Meanwhile, Toc132/Toc120 together with Toc34 form an alternative TOC complex that is responsible for the import of non-photosynthetic/housekeeping proteins. However, the clients of Toc159/Toc33 and Toc132/120/Toc34 receptors may largely overlap and/or complement one another when the activity of one receptor is reduced. The nature of the TIC complex and its associated molecular motors remains controversial. In the model plant Arabidopsis, the newly identified 1-MD TIC complex contains the channel-forming Tic20 (Tic20-I), the chloroplast-encoded Tic214/Ycf1, Tic100, and Tic56. The molecular motor that hydrolyzes ATP to provide energy for the passage of preproteins through the TIC complex has been identified. It includes another chloroplast-encoded large open reading frame, Ycf2, the IEM-localized FtsHi, and NAD-malate dehydrogenase (NAD-MDH). The previously identified chaperones (cpHSC70, HSP90C, and HSP60) that associate with the Tic110 scaffold, may act downstream at the late stage of the cotranslocational folding process. An alternative TIC complex may exist, which comprises the Tic20 isoform, Tic20-IV, and other unidentified components without Tic214/Ycf1, as the plastids still contain non-photosynthetic chloroproteins when plastid translation is fully blocked, which abolishes chloroplast-encoded Tic214/Ycf1 and Ycf2. It should be noticed that Tic214/Ycf1 is absent in some monocots such as Poaceae. The cytosolic factor AKR2 and the small HSP, HSP17.8, facilitate the targeting of OEM-localized proteins. Toc75 may participate in this process.