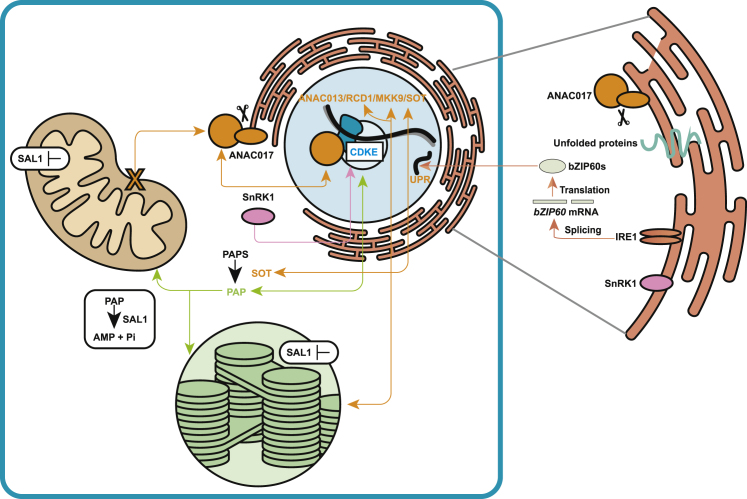
Figure 2.
Interactions between mitochondrial and chloroplast retrograde signaling pathways.
Release of ANAC017 from the ER is initiated by perturbation of mitochondrial function; after translocation to the nucleus, ANAC017 activates the expression of target genes. ANAC017 binds directly to the promoters of RCD1, MKK9, and SOT, which have been shown to participate directly in chloroplast retrograde signaling pathways (see text for details). SAL1-PAP signaling has been extensively characterized as a chloroplast retrograde pathway, but emerging experimental evidence from complementation of a sal1 mutant with a mitochondria-only targeted protein shows interaction with mitochondrial signaling. CDKE has been shown to regulate AOX1a and a variety of other genes at a transcriptional, and for AOX1a post-transcriptional, level. It interacts with SnRK1, which displays a dynamic subcellular localization, with cytosolic, ER, and nuclear localizations reported. ANAC017 is necessary for the ER UPR response and ER-located RNA splicing enzyme inositol-requiring enzyme 1 that is involved in the alternative splicing of bZIP60.
ER, endoplasmic reticulum; UPR, unfolded protein response; ANAC017, Arabidopsis NAC transcription factor 017; ANAC013, Arabidopsis NAC transcription factor 013; RCD1, radical cell death 1; MKK9, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 9; SOT, sulphotransferase; CDKE, cyclin-dependent kinase E1; SnRK1, SNF1-related kinase 1; PAPS, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate; PAP, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; IRE1, inositol requiring 1; bZIP60, basic region/leucine zipper motif 60.