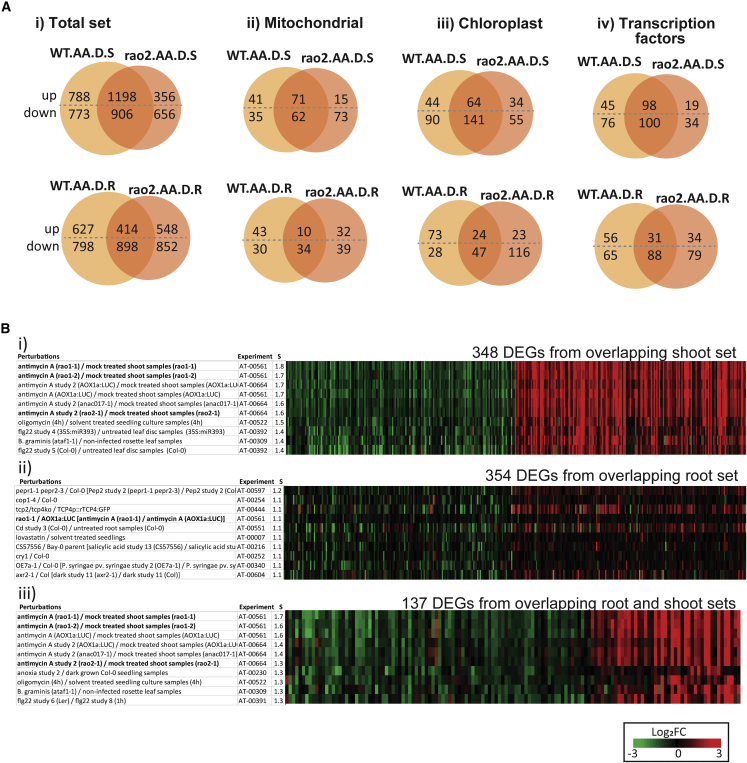
Figure 2.
Characterization of the antimycin A-specific response in dark conditions.
(A) Venn diagrams showing numbers of overlapping DEGs between wild-type and ANAC017 mutant (rao2) lines after antimycin A (AA) treatment in the dark (D) in shoots (S) and roots (R).
(B) Fold changes of genes differentially expressed in response to AA in the dark in shoots and roots were analyzed using the signature tool in Genevestigator to identify studies (perturbations) that showed the most similar fold-change responses; similarity scores (S) are indicated. Two hundred randomly selected upregulated genes and 200 randomly selected downregulated genes from the overlapping total sets in (A) were used. (i) Shoots and (ii) roots were viewed (348 and 354 of these matched probesets from the database in shoots and roots, respectively). (iii) The overlapping set of genes responsive in both roots and shoots to antimycin A treatment in the dark from (B) were also examined using the signature tool (137 matched probesets). The top 10 studies in which the most similar fold-change responses were observed for these genes are shown. Each subset contained antimycin A-treated rao mutant studies (indicated in bold).