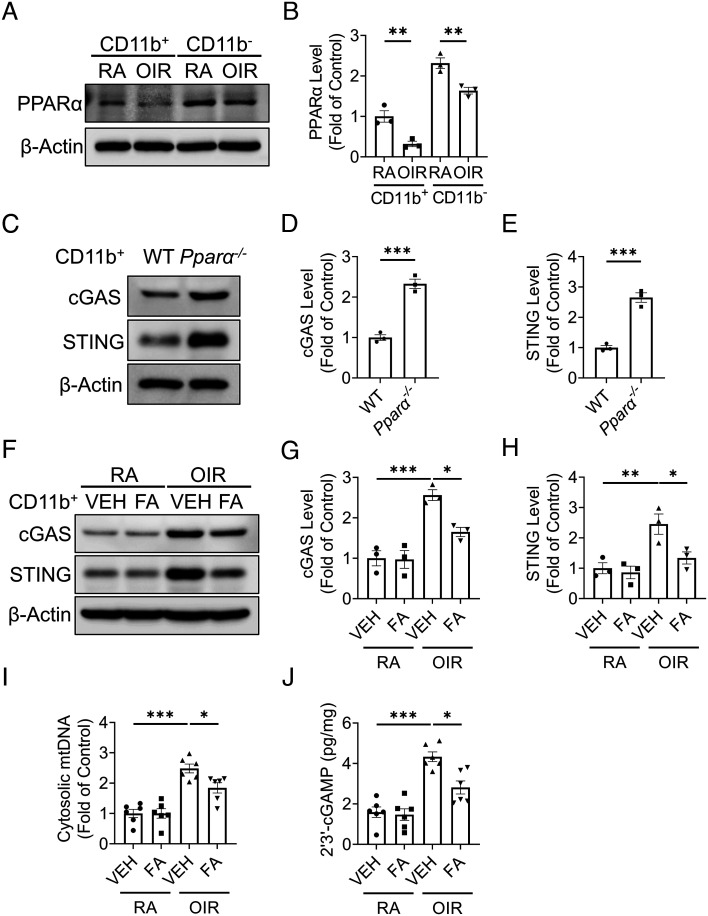
Fig. 7.
PPARα modulated cGAS-STING signaling in the OIR model. Myeloid cells (CD11b+) and non-myeloid cells (CD11b−) were isolated from the retinas using the MACS method. A: Representative images of western blotting for PPARα in the myeloid cells and non-myeloid cells from the RA and OIR retinas at P17. B: Protein levels of PPARα in (A) were quantified by densitometry and normalized by β-actin levels (n = 3). C: Representative images of western blotting for cGAS and STING in myeloid cells from WT and Pparα−/− retinas at P17 at RA. D and E: Protein levels of cGAS (D) and STING (E) in (C) were quantified by densitometry and normalized by β-actin levels (n = 3). F: Representative images of western blotting for cGAS and STING in retinal myeloid cells isolated from RA controls and OIR mice treated with vehicle (VEH) or (FA, 25 mg/kg/day from P12 to P17). G and H: Protein levels of cGAS (G) and STING (H) in (F) were quantified by densitometry and normalized by β-actin levels (n = 3). I: Cytosolic mtDNA levels in retinal myeloid cells isolated from RA controls and OIR mice treated with VEH or FA. Cytosolic mtDNA levels were presented as the fold of VEH-treated RA group (n = 6). J: Levels of 2′3′-cGAMP were measured in retinal myeloid cells isolated from RA control and OIR mice treated with VEH or FA at P17 using 2′3′-cGAMP ELISA kit (n = 6). Data were presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.