Fig. 8.
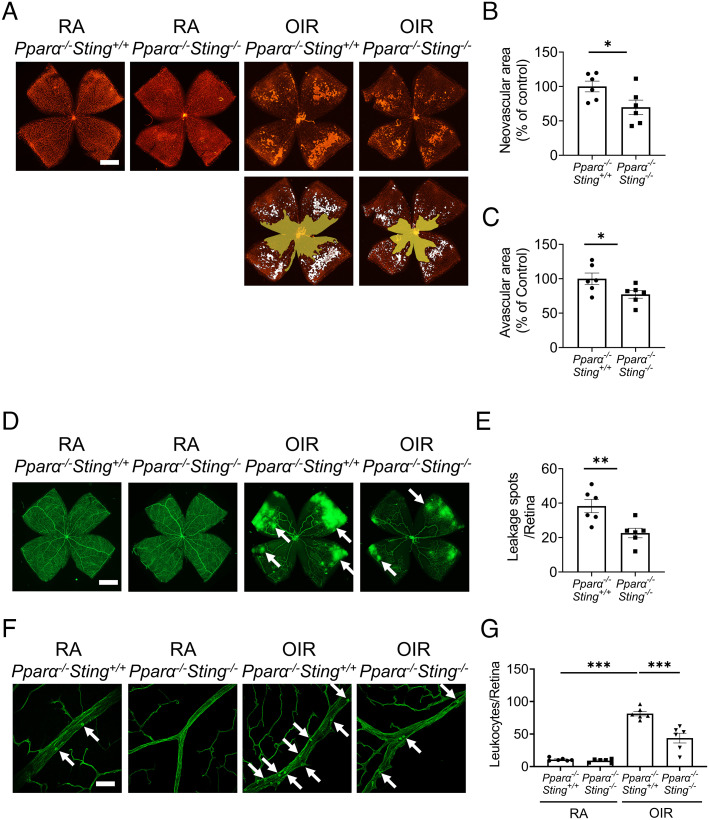
Knockout of Sting ameliorated retinal vascular pathologies in Pparα−/− OIR mice. A: Representative images of isolectin-stained retinal flat mounts from Pparα−/−Sting+/+ mice and Pparα−/−Sting−/− littermates in RA control and OIR groups at P17. (Scale bar: 1 mm.) The neovascular areas and avascular areas were labeled with white color and yellow color, respectively. B and C: The quantification of neovascular areas and avascular areas in (A) (n = 6). D: Representative images of retina flat mounts from Pparα−/−Sting+/+ mice and Pparα−/−Sting−/− littermates perfused with FITC-dextran. (Scale bar: 1 mm.) The white arrows indicated the vascular leakage spots. E: Vascular leakage spots in (D) were quantified (n = 6). F: Representative images of retinal leukostasis from Pparα−/−Sting+/+ mice and Pparα−/−Sting−/− littermates in RA control and OIR mice at P17. (Scale bar: 20 µm.) The white arrows indicated the adherent leukocytes. G: Quantification of adherent leukocytes in retinal flat mounts in (F) (n = 6). Data were presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.