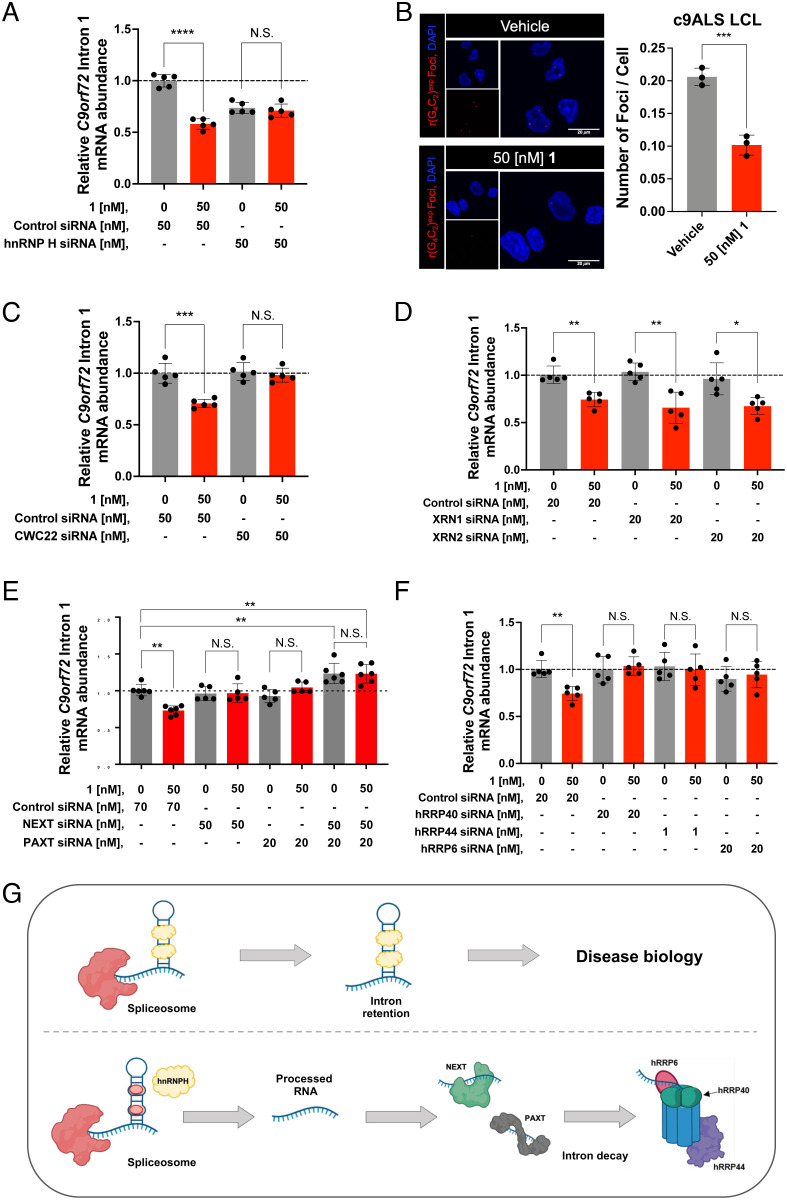
Fig. 3.
Compound 1 selectively degrades C9orf72 intron 1 via the nuclear exosome and RNA carrier proteins. (A) Effect of co-treating a c9ALS patient-derived iPSC line with 1 and an siRNA targeting hnRNP H, on the abundance of C9orf72 intron 1, as determined by qRT-PCR using intron 1-specific primers (n = 1 c9ALS iPSC line, five replicates per concentration). (B) Left: Representative images of r(G4C2)exp foci in a c9ALS patient-derived LCL imaged by confocal microscopy treated with vehicle or 1. Right: Quantification of relative number of r(G4C2)exp foci per cell (n = 1 c9ALS LCL, three replicates; 200 nuclei counted per biological sample). (C) Effect of co-treating c9ALS patient-derived iPSCs with 1 and an siRNA targeting CWC22, on the abundance of C9orf72 intron 1, as determined by qRT-PCR using intron 1-specific primers (n = 1 c9ALS iPSC line, five replicates per condition). (D) Effect of co-treating c9ALS patient-derived iPSCs with 1, and siRNAs targeting either XRN1 or XRN2 on the abundance of C9orf72 intron 1, as determined by qRT-PCR using intron 1-specific primers (n = 1 c9ALS iPSC line, five replicates per condition). (E) Effect of treating c9ALS patient-derived iPSCs with 1, siRNAs targeting NEXTPAXT, or both, on the abundance of C9orf72 intron 1, as determined by qRT-PCR using intron 1-specific primers (n = 1 c9ALS iPSC line, five replicates per condition). (F) Effect of co-treating c9ALS patient-derived iPSCs with 1 and siRNAs targeting various components of the exosome (hRRP6, hRRP40, or hRRP44), on the abundance of C9orf72 intron 1, as determined by qRT-PCR using intron 1-specific primers (n = 1 c9ALS iPSC line, five replicates per condition). (G) Schematic representation of the RNA decay mechanism of action upon treatment with 1. RNA abundance was measured and quantified relative to GAPDH. Vehicle indicates 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, as determined by an Unpaired t test with Welch’s correction. Error bars are repoted as SD.