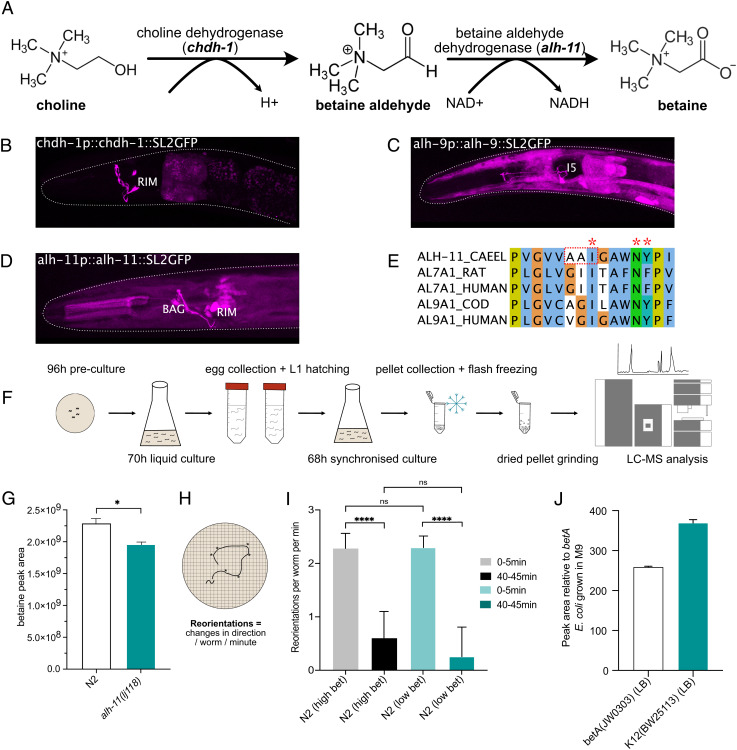
Fig. 3.
Neuronal C. elegans betaine synthesis pathway involves alh-11. (A) Schematic of the betaine biosynthesis pathway and putative enzymes involved in each stage. (B–D) Fluorescent reporter of intercistonically spliced GFP driven under the promoter and genomic sequence of the putative betaine synthesis enzymes chdh-1, alh-9, and alh-11. (E) Cropped alignment of the substrate-binding region of C. elegans ALH-11 and related genes from rat, human and cod. Stars highlight conserved residues required for substrate and NAD+ binding as described by ref. 27, residues within the red box are mutated in alh-11(lj118) from AAI to --V, the full alignment can be found in SI Appendix, Fig. S1B. (F) Schematic describing the experimental procedure for metabolite extraction paired with LC–MS analysis in C. elegans preparations. (G) Mass spectrometry analysis of betaine content in C. elegans wild-type or alh-11 mutant preparation. The data show peak area for betaine. Error bars represent SEM of three samples per genotype, *P < 0.05 calculated by unpaired t-test. (H) Schematic representing the experimental design. (I) Food search behavior as calculated by reorientations per worm per minute in N2 worms grown under betaine-deficient conditions using the strain betA(JW0303), grown in M9 media, or betaine-containing Lennox Broth (LB) media. N = 75–133 worms per condition. Bar charts showing median with 95% CI and significance test using the Kruskal–Wallis test *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005. (J) Relative betaine amount detected using quantitative mass spectrometry in the betA(JW0303) and K12(BW25113) strains grown in LB media to the betA grown in M9 media.