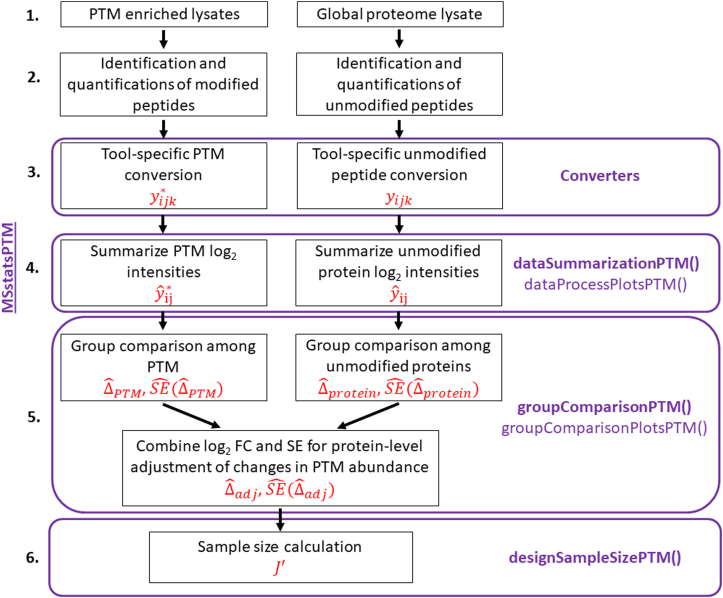
Fig. 3.
The MSstatsPTM workflow. The names of the MSstatsPTM R functions used for each step are highlighted in purple and the output notations are highlighted in red. The workflow begins with the acquisition of the enriched and global proteome lysates. The package is applicable to label-free data acquisitions, such as DDA, DIA, SRM, and label-based data acquisitions, such as TMT. It takes as input lists of identified and quantified spectral features for the PTM and for the unmodified portion of the protein, produced by spectral processing tools such as MaxQuant, Progenesis, or Spectronaut. Conversion, summarization and statistical modeling are performed separately for the PTM and for the unmodified portions of the proteins. Steps 4 and 5 leverage the summarization and modeling functions from MSstats and MSstatsTMT. Model-based summaries are combined to adjust the changes in the PTM abundance for changes in abundance of the unmodified portion of the protein. Finally, sample size calculation for future experiments can be performed using the modeling output. DDA, data-dependent acquisitions; DIA, data-independent acquisition; PTM, posttranslational modification; SRM, selected reaction monitoring.