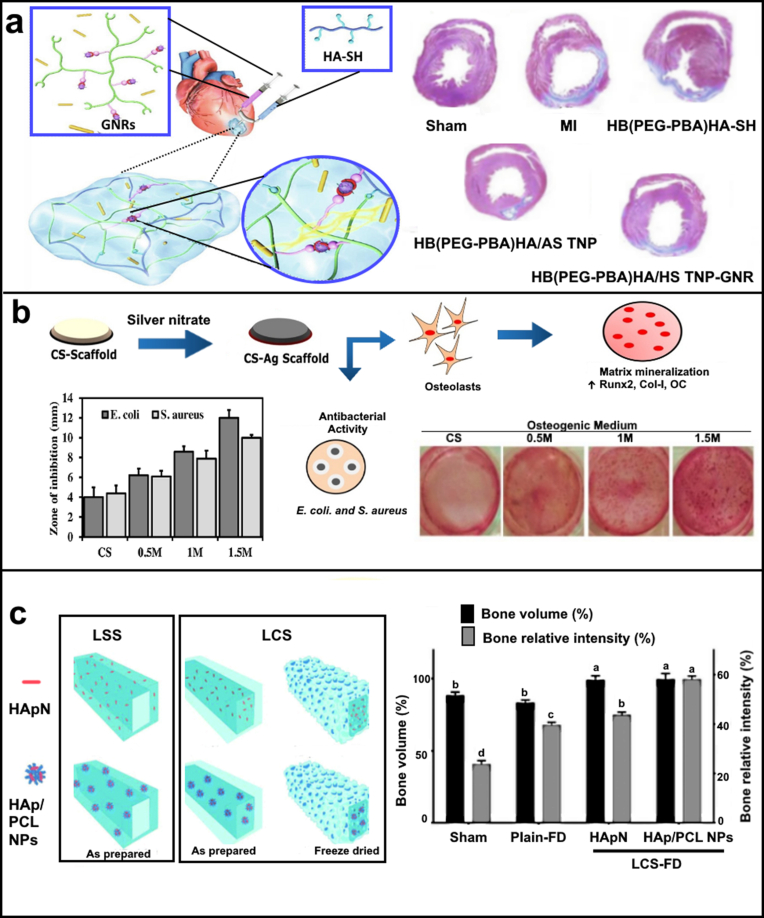
Fig. 3.
(a) Depicts an injectable hydrogel hybrid for cardiac regeneration comprising of phenylboronic acid hyperbranched polymers and thiol hyaluronic acid for loading Astragaloside IV and gold nanorods. The treatments of hydrogels significantly resisted these pathological and morphological changes, with the highest improvement by HB (PEG-PBA)/HA-SH/AST NPs/GNRs. Reproduced from Ref. [59]. (b) Composite scaffolds fabricated utilising CS and AgNPs. Graph shows that CS-Ag scaffolds exhibited greater antibacterial activity compared to naïve CS scaffolds against both E. coli and S. aureus. CS itself possesses antibacterial activity and it is greatly enhanced by the presence of silver nanoparticles. Alizarin red stained photographic images showed that cells grown on CS-Ag-1 M and CS-Ag 1.5 M scaffold films showed more prominent nodules compared to cells grown on other scaffold films. Reproduced from Ref. [67]. (c) Two different designs were realised for loaded-core scaffolds (LCS) and loaded-shell scaffolds (LSS), where PPI-4 was used to print plain shell and core phases for LCS and LSS, respectively, while HAp-ink and HAp/PCL NP ink were separately used to print core and shell phases in LCS and LSS, respectively. Immense tissue cavitation could be recognised in deeper layers as radiolucent regions among areas of higher radiopacity, greatly according with the significantly (p ≤ 0.05) lower percentage bone relative intensity recorded for the sham group compared to the Plain-FD group. Reproduced from Ref. [68].