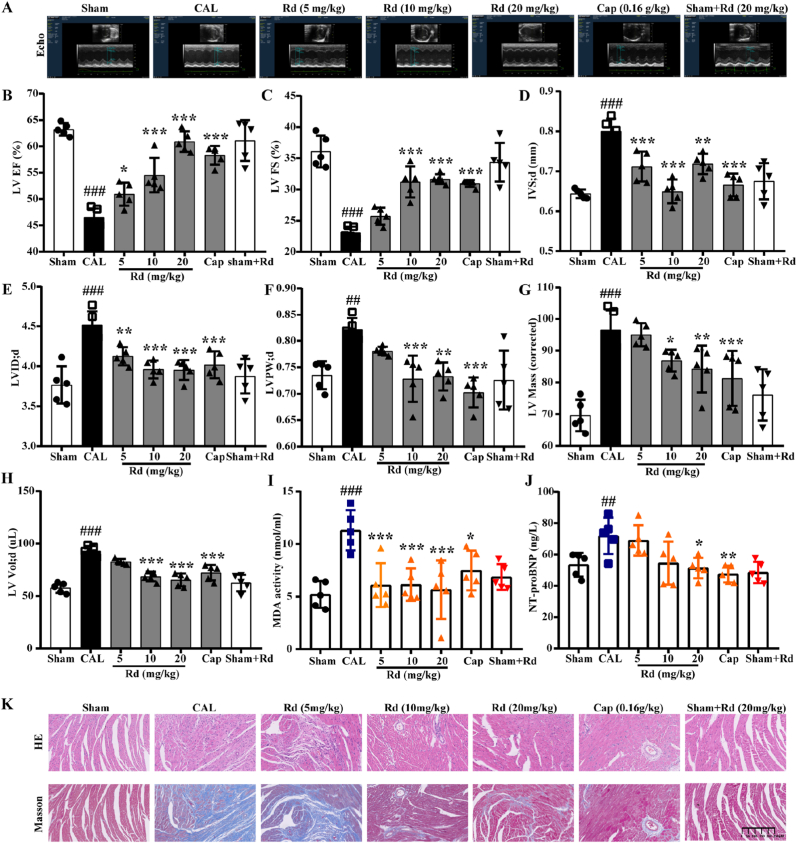
Fig. 1.
Ginsenoside Rd ameliorated myocardial injury in CAL-induced HF mice. The mice were divided into seven groups randomly. The CAL group, ginsenoside Rd group and Captopril group were performed to CAL and treated with NS, ginsenoside Rd (5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg) and Captopril (0.16 g/kg), respectively. The sham group was treated with NS. (A) Representative M-mode echocardiograms. (B) The effect of ginsenoside Rd on LV EF, (C) LV FS, (D) IVS; d, (E) LVID; d, (F) LVPW; d, (G) LV Mass, (H) LV Vol; d changes in CAL performed mice evaluated by echocardiographic (n = 5). The MDA content (I) and NT-proBNP levels (J) in serum were detected by Elisa (n = 5). (K) Profiles of heart tissues in mice treated with ginsenoside Rd (HE staining and Masson staining) (n = 3). Values are expressed as the means ± SD. One-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett's post hoc test was used for statistical analysis. ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. Sham; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. CAL. Cap = Captopril.