Supplemental Figure S1.
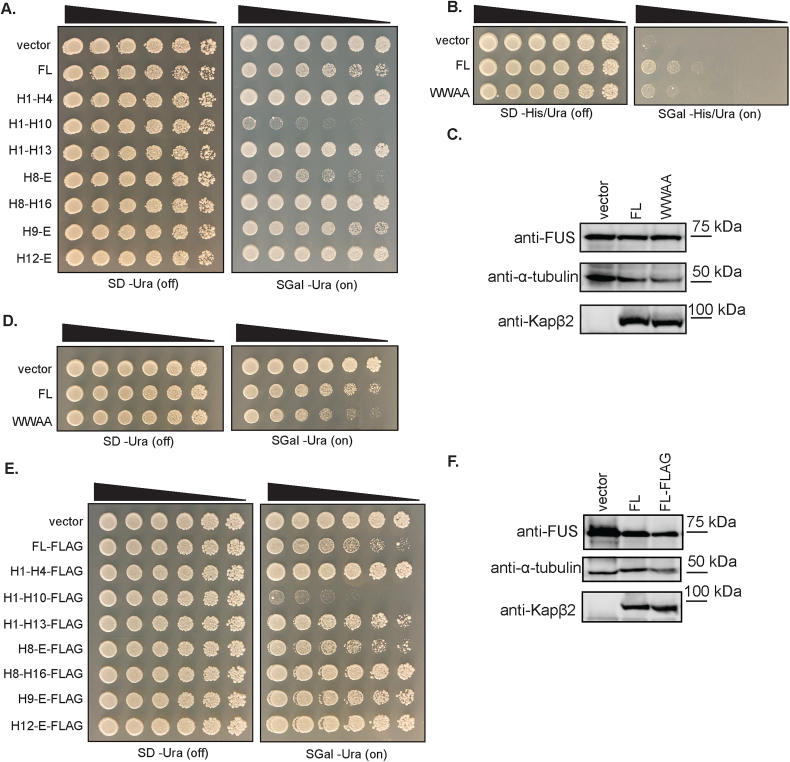
Kapβ2 and truncation variants are typically not toxic and robustly expressed in yeast.A, Δhsp104 yeast were transformed with the indicated galactose-inducible Kapβ2 construct and serially diluted 3-fold onto agar plates with either glucose (expression off) or galactose (expression on) to assess toxicity of each Kapβ2 construct on its own. H1-H10 exhibits toxicity relative to vector, and FL Kapβ2, H8-E, and H9-E show slight toxicity. B, Δhsp104 yeast with galactose-inducible FUS integrated into the strain were transformed with galactose-inducible FL Kapβ2 or Kapβ2W460A:W730A (WWAA) and serially diluted 3-fold onto agar plates with either glucose (expression off) or galactose (expression on) as the carbon source. Media was prepared lacking histidine and uracil; the FUS plasmid contains genetic information for synthesizing histidine, and the Kapβ2 plasmid contains the genetic information for synthesizing uracil. In the absence of any Kapβ2, FUS expression is very toxic. This toxicity can be mitigated by the expression of full-length (FL) Kapβ2, but not the Kapβ2W460A:W730A (WWAA) mutant. C, a Western blot probing yeast expressing FUS and either FL Kapβ2WT or the WWAA mutant with an anti-Kapβ2 antibody shows that neither FUS nor Kapβ2 expression changes as a function of Kapβ2 variant expression relative to the α-tubulin loading control. D, Δhsp104 yeast with no disease-associated protein integrated into the strain were transformed with either vector, FL Kapβ2 or the Kapβ2W460A:W730A (WWAA) mutant and serially diluted 3-fold onto agar plates with either glucose (expression off) or galactose (expression on) as the carbon source to test for toxicity of WWAA on its own. WWAA is slightly more toxic than the WT FL protein. E, Δhsp104 yeast with no disease-associated protein integrated into the strain were transformed with the indicated galactose-inducible FLAG-tagged Kapβ2 truncation and serially diluted 3-fold onto agar plates with either glucose (expression off) or galactose (expression on) as the carbon source to test for toxicity of each truncation on its own. As with the untagged variants, H1-H10-FLAG is more toxic relative to vector. H8-E-FLAG and H9-E-FLAG show less intrinsic toxicity than their untagged counterparts. F, probing yeast expressing FUS and either tagged or untagged FL Kapβ2 with an anti-Kapβ2 antibody shows that, compared to the untagged protein levels, the addition of the FLAG-tag does not affect FL Kapβ2 expression.