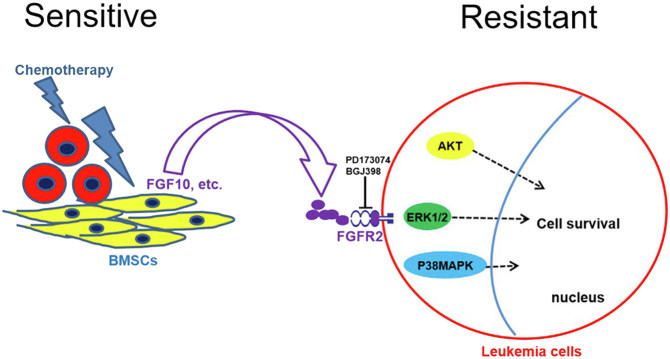
Figure 8.
Model of drug-resistance effects of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) in response to antileukemia drugs. Antileukemia drugs activate a DNA damage response (DDR) in BMSCs and induce diverse proteins that promote survival of AML cell lines via progrowth signaling pathways. Drug-induced β-catenin activation in damaged BMSCs regulates FGF10 secretion–promoting survival of AML cell lines by activating FGFR2, P38 MAPK, AKT, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Blocking FGF10–FGFR2 signaling with PD173074 and BGJ398 reverses the prosurvival effects of BMSCs on AML cell lines by inhibiting P38 MAPK, AKT, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. AML, acute myeloid leukemia; ERK1/2, extracellular signal–regulated kinase 1/2; FGF10, fibroblast growth factor-10; FGFR2, fibroblast growth factor receptor 2; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase.