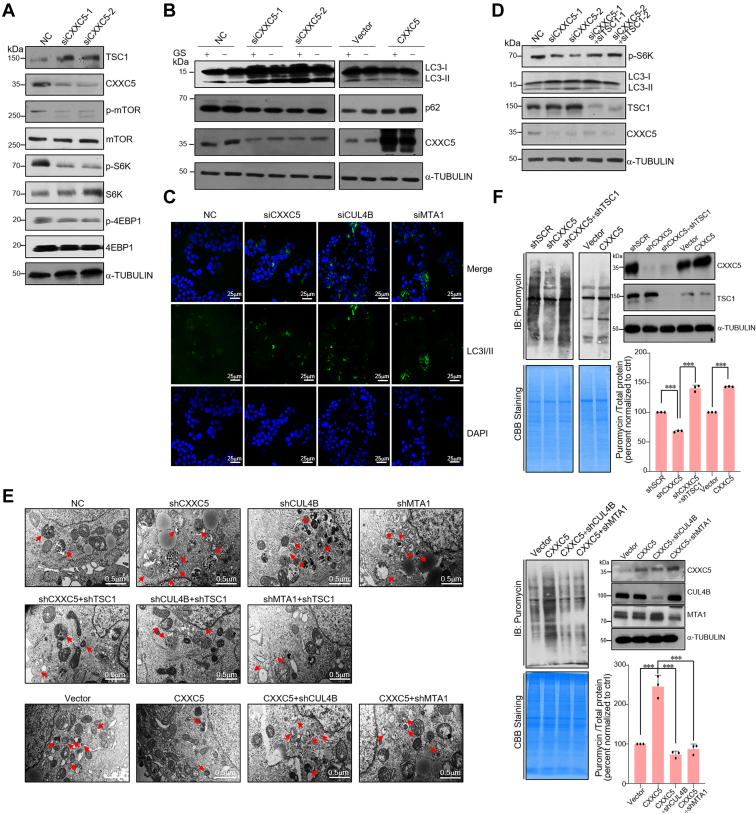
Figure 4.
CXXC5 regulates mTOR signaling and impacts autophagy and protein synthesis by transcriptional repression of TSC1 (Fig. S1). A, after transfection of different groups of CXXC5 siRNAs into MCF-7 cells, Western blotting (WB) was used to detect the indicated protein expression levels. B, MCF-7 cells with CXXC5 overexpression or knockdown were treated with or without 4 h glucose starvation (GS). Total cellular proteins were prepared and analyzed for the indicated proteins expression by WB. C, CXXC5, CUL4B, or MTA1 siRNAs were transfected into MCF-7 cells. The expression level of LC3I/II was detected by immunofluorescence microscopy (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). D, the MCF-7 cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs were assayed for autophagy markers by WB. E, MCF-7 cells stably expressing the specific expression constructs and indicated shRNA lentiviruses were assayed for autophagosomes and autolysosomes by TEM. F, MCF-7 cells stably expressing the specific expression constructs and indicated shRNA lentiviruses were assessed for their ability for de novo protein synthesis using antipuromycin immunoblotting and pulsed with a final concentration of 1 μM puromycin for 30 min. Coomassie blue staining represented the total proteins. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; TEM, transmission electron microscopy; TSC1, tuberous sclerosis complex subunit 1.