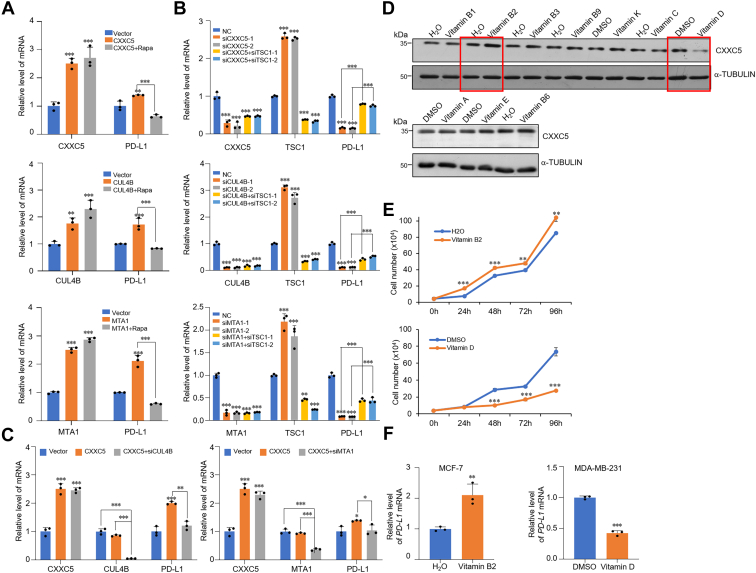
Figure 6.
CXXC5 contributes to immune escape ability of cancer cells and is bimodally regulated by vitamins.A, the level of PD-L1 mRNA in CXXC5, CUL4B, or MTA1 overexpression or/and 25 nM rapamycin-treated MDA-MB-231 cells was detected using RT–qPCR analysis. B, the mRNA level of PD-L1 in MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with control siRNA, CXXC5, CUL4B, MTA1 or/and co-ransfected with TSC1 siRNA was measured by RT–qPCR. C, the mRNA level of PD-L1 in CXXC5-overexpressing MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with CUL4B or MTA1 siRNA was measured by RT–qPCR. D, CXXC5 expression level in MCF-7 cells with different vitamin treatments was analyzed by Western blotting. E, growth curve assays of MCF-7 cells under different vitamin treatments. F, MCF-7 cells were treated with 266 nM vitamin B2, MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 100 nM vitamin D, and the expression of PD-L1 was detected by RT–qPCR. PD-L1, programmed cell death–ligand protein 1; qPCR, quantitative PCR; TSC1, tuberous sclerosis complex subunit 1.