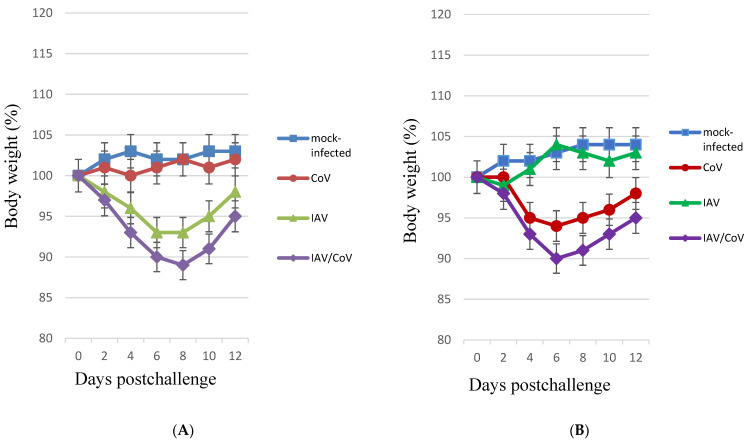
Figure 4.
Body weight changes in monoinfected and coinfected with IAV and SARS-CoV-2 animals. (A) Body weight changes in monoinfected and coinfected with IAV and SARS-CoV-2 ferrets. “CoV (SARS-CoV-2)”—on Day 0, the ferrets were intranasally challenged with SARS-CoV-2 (3 × 105 TCID50); “IAV”—on Day 0, the ferrets were intranasally challenged with IAV (102 TCID50); “IAV/CoV”—on Day 0, the ferrets preinfected (2 days earlier) with IAV (102 TCID50) were intranasally challenged with SARS-CoV-2 (3 × 105 TCID50); “mock-infected”—on Day 0, the ferrets were intranasally inoculated with PBS. n = 4. (B) Body weight changes in monoinfected and coinfected with IAV and SARS-CoV-2 hamsters. “CoV SARS-CoV-2)”—on Day 0, the hamsters were intranasally challenged with SARS-CoV-2 (104 TCID50); “IAV”—on Day 0, the hamsters were intranasally challenged with IAV (2 × 103 TCID50); “IAV/CoV”—on Day 0, the hamsters preinfected (4 days earlier) with IAV (2 × 103 TCID50) were intranasally challenged with SARS-CoV-2 (104 TCID50); “mock-infected”—on Day 0, the hamsters were intranasally inoculated with PBS. n = 8 at 0 dpi to 6 dpi; n = 4 at 7 dpi to 12 dpi, as 4 animals were sacrificed. The values represent the means ± SDs of individual animals. Student’s t-test was used for two-group comparisons. * p < 0.05.