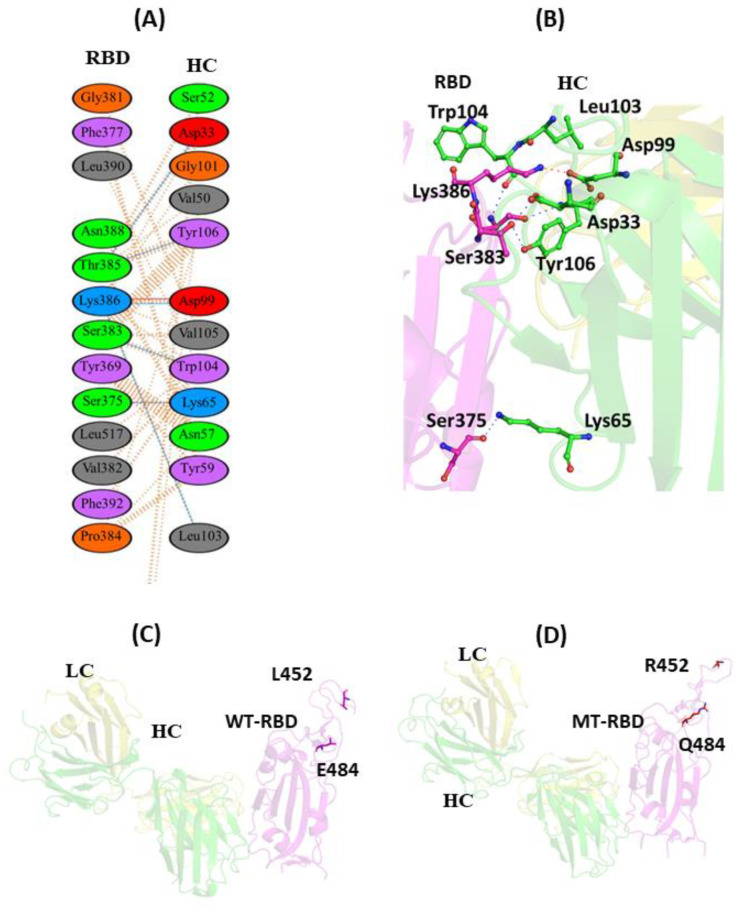
Figure 5.
Protein–protein interaction of RBD with EY6A mAb: (A) 2D interaction diagram of binding interface of WT-RBD with EY6A antibody; (B) 3D cartoon representation of intermolecular interaction of E484 residue of RBD with HC of EY6A antibody; (C) cartoon representation of WT-RBD with EY6A antibody. The residues L452 and E484 are represented in sticks. These residues lie far away from EY6A binding site and do not participate in forming intermolecular contact with mAb; (D) Cartoon representation of MT-RBD with EY6A mAb. R452 and Q484 residues of RBD are shown in sticks. These residues also do not interact with EY6A antibody. RBD represents receptor-binding domain, HC represents heavy chain of monoclonal antibody, while LC represents light chain of mAb.