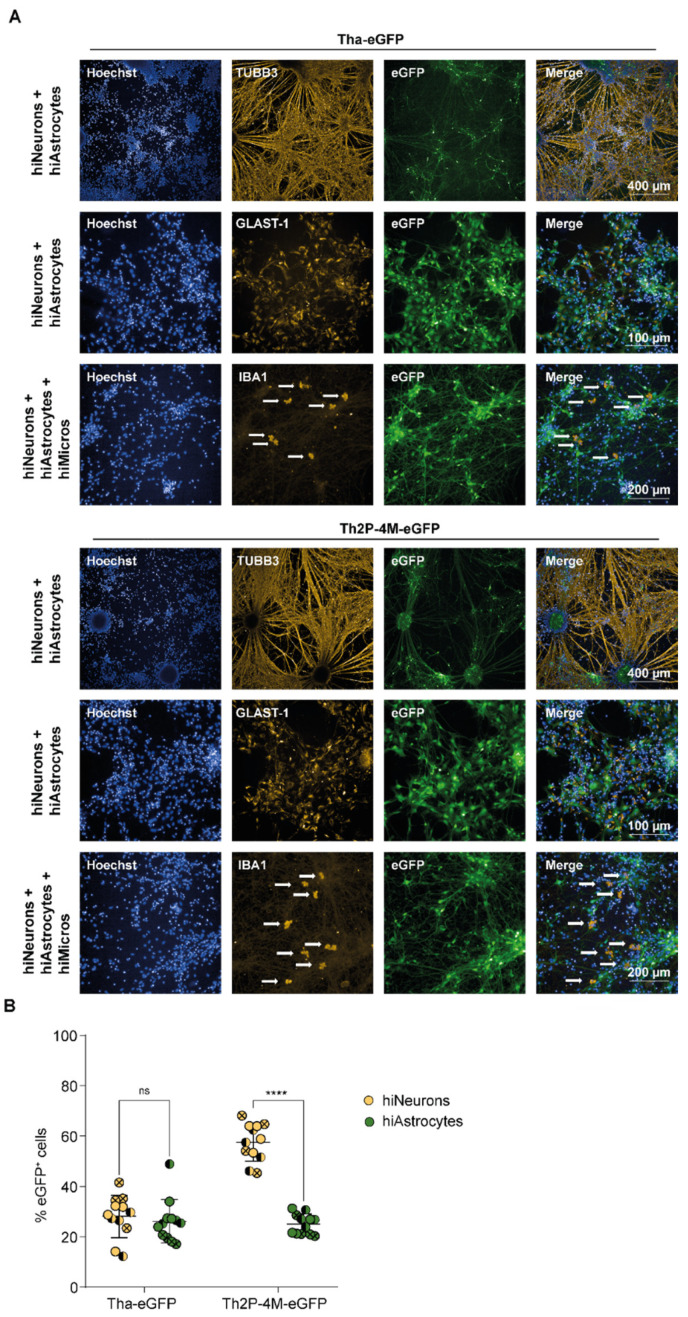
Figure 2.
Whereas hiNeurons and hiAstrocytes are highly susceptible to Tha-eGFP and Th2P-4M-eGFP infection, hiMicros are resistant to Tha-eGFP or Th2P-4M-eGFP infection in vitro. (A) Representative immunofluorescence pictures of hiNeurons, hiAstrocytes, and hiMicros upon infection with Tha-eGFP and Th2P-4M-eGFP. IBA1+ hiMicros are indicated with an arrow. (B) Quantification of eGFP+ cells in Tha-eGFP-infected triple cultures consisting of hiNeurons, hiAstrocytes, and hiMicros. Every dot represents imaging of one well of a 96-well-plate (approx. 1 × 104 cells/well). Bars show mean ± SD. Different colours present different cell types, and different symbol shapes indicate the three technical replicates performed. Hoechst binds to regions of DNA in the minor groove visualizing cellular DNA. Percentages of eGFP+ cells were analysed using a mixed model with the replication factor as a random effect, followed by multiple comparisons corrected by Tukey’s method (**** adjusted p-value < 0.000025, ns = no significant difference was observed). (A,B) Prior to infection, cultures consisted of hiNeurons (71.0%), hiAstrocytes (18.4%), and hiMicros (10.6%, Table S5). Cells were infected with Tha-eGFP or Th2P-4M-eGFP (MOI 0.5) and imaged at 48 h post-infection. All experiments were performed three times (n = 3) independently. eGFP = Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein; GLAST-1 = Glutamate Aspartate Transporter-1; IBA1 = Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1; TUBB3 = Class III Beta-Tubulin.