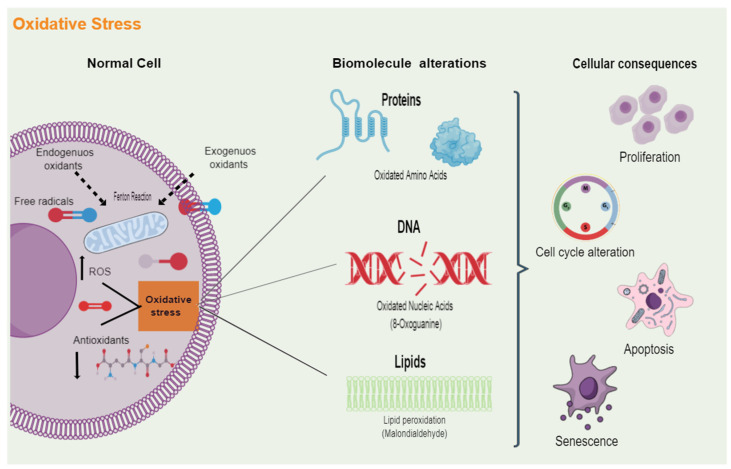
Figure 1.
Cellular damage induced by oxidative stress. Multiple endogenous and exogenous sources produce free radicals, which are molecules that contain one or more unpaired electrons. When an imbalance arises between the oxidative molecules present in cells, such as reactive oxygen species (ROS), and the antioxidant defenses that neutralize and eliminate these reactive radicals, oxidative stress is generated. Excess oxidative stress can play a dominant role in protein, cell membrane phospholipids, and DNA damage. The attack of ROS on these biomolecules alters their functions and, ultimately, will lead to the dysregulation of different cellular processes, including proliferation, cell cycle, cell death, and senescence.