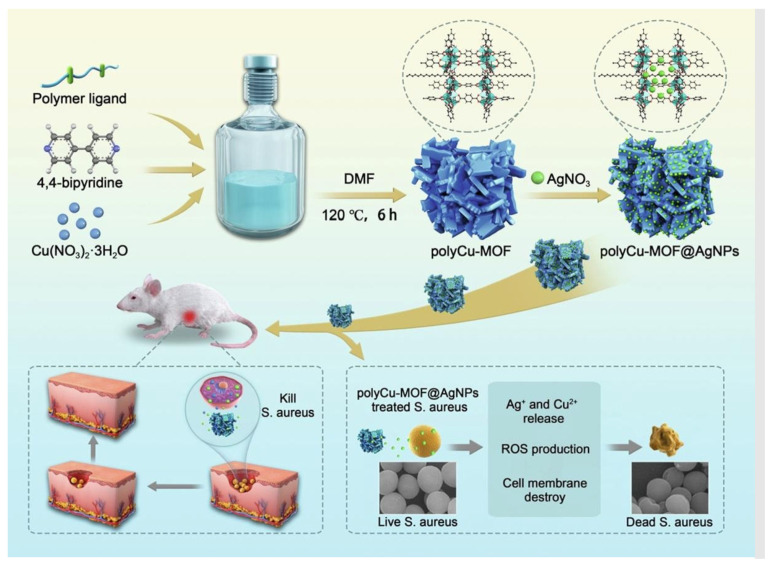
Figure 20.
Scheme showing the synthesis of PolyCu-MOF@AgNPs and an illustration of the antibacterial properties of the product. The scheme shows in situ formation of loaded MOF/hybrid composites to create polyCu-MOF. The MOF composites are then post-synthetically treated with AgNO3 to yield polyCu-MOF@AgNPs. In vivo experiments on mice show improved healing of bacteria-infected skin wounds and allow for the regeneration of collagen and the healing of damaged tissues. SEM images of in vitro treated S. aureus showing the change of morphology of dead S. aureus and listing the antimicrobial mechanisms as Ag+ and Cu2+ release, ROS production as well as cell membrane destruction. Reproduced with permission from [187].