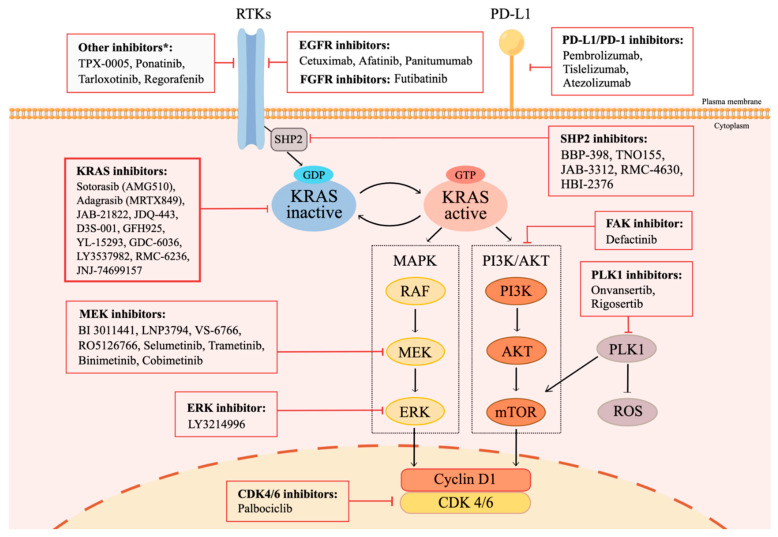
Figure 1.
Signaling Pathways Related to KRAS Mutations, and Potential Treatment Strategies. * KRAS switches between a guanosine diphosphate (GDP)-bound inactive state and a guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-bound active state. Normally, KRAS is bound to GDP and remains inactive. Activation through receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) leads to the activation of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) family, which subsequently triggers the exchange between GDP and GTP. GTP-bound active KRAS transduces downstream signals, including mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway, which are responsible for cell proliferation, cell cycle regulation, cell survival, and cell differentiation. The treatment approaches of KRAS mutant patients include therapies targeting KRAS, and factors involved in the KRAS mutation pathways, such as RTKs, SHP2, PI3K pathway elements, MAPK pathway elements, and CDK4/6. ICIs are also included, considering the potential effect on KRAS mutant patients. This figure was created using Figdraw.