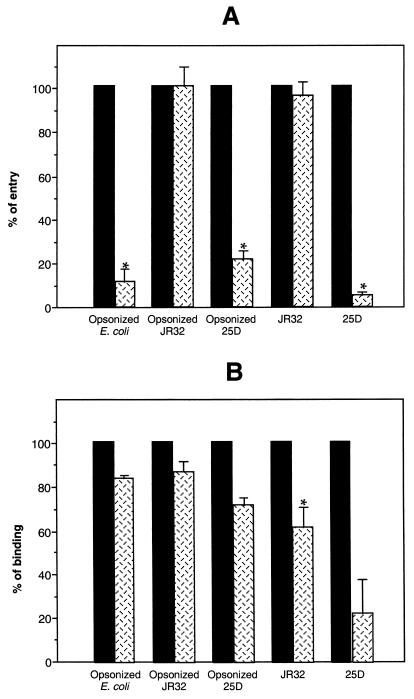
FIG. 1.
Effect of wortmannin on bacterial phagocytosis and binding. Differentiated U937 cells were treated with 100 nM wortmannin ( ) or not treated (■) and infected with opsonized or nonopsonized L. pneumophila wild-type (JR32) or avirulent mutant (25D) or with opsonized E. coli. (A) Phagocytosis by wortmannin-treated cells was expressed as a percentage of phagocytosis by untreated cells. (B) Bacterial binding to wortmannin-treated cells was expressed as a percentage of bacterial binding to untreated cells. Values of phagocytosis and binding obtained in the presence of wortmannin were expressed as a percentage of the values obtained in absence of treatment (defined as 100%). Error bars represent standard errors. Asterisks represent values for treated cells statistically different from values for untreated cells with a value of P < 0.05 as determined with the Student t test.
) or not treated (■) and infected with opsonized or nonopsonized L. pneumophila wild-type (JR32) or avirulent mutant (25D) or with opsonized E. coli. (A) Phagocytosis by wortmannin-treated cells was expressed as a percentage of phagocytosis by untreated cells. (B) Bacterial binding to wortmannin-treated cells was expressed as a percentage of bacterial binding to untreated cells. Values of phagocytosis and binding obtained in the presence of wortmannin were expressed as a percentage of the values obtained in absence of treatment (defined as 100%). Error bars represent standard errors. Asterisks represent values for treated cells statistically different from values for untreated cells with a value of P < 0.05 as determined with the Student t test.