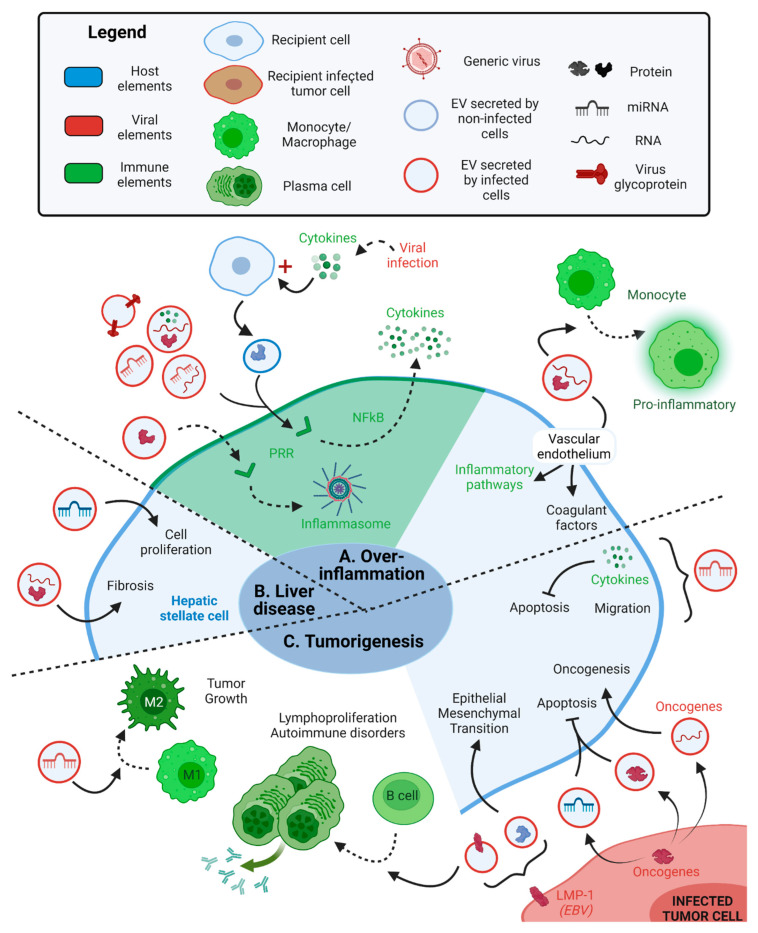
Figure 4.
EVs mediate virus-associated disorders. (A) EVs secreted by both infected and non-infected cells lead to over-inflammation. Virus-EVs containing viral proteins can indirectly activate the inflammasome in immune cells, supporting over-inflammation [HIV [106]. Virus-EVs containing viral proteins, glycoproteins, miRNAs and or mRNAs can also activate the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines through PRR recognition in immune cells, leading to chronic inflammation [HIV-1 [72,102,103], EBV [61], Ebola virus [93], HTLV-1 [105]. Virus infection induces the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the environment, which activate the secretion of EVs by non-infected cells. These EVs contain host proteins that activates the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by recipient immune cells through PRR recognition [DV [107]. Virus-EVs containing viral proteins and mRNAs induce the phenotype switch of recipient monocytes into a pro-inflammatory phenotype and promote inflammatory and coagulant pathways in recipient endothelial cells [Zika virus [57]. (B) EVs secreted by infected cells are associated with liver disease. Virus-EVs containing viral proteins and RNA or host miRNA are integrated by hepatic stellate cells and either stimulate cell proliferation or fibrosis in the liver [HBV [108], HCV [109]. (C) EVs secreted by infected tumor cells enhance tumorigenesis. Infected tumor cells expressing oncogenes can be associated with the secretion of virus-EVs transferring viral oncogene proteins [HTLV-1 [105] or host miRNAs [HPV-16 [110,111] to recipient cells, which inhibit apoptosis. These virus-EVs can also contain the viral oncogene mRNA, which induces oncogenesis in recipient cells [HPV-16 [112]. In EBV-infected cells, expression of LMP-1 viral protein induces secretion of EVs containing host proteins that induce the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in recipient cells and promote tumor migration [113]. EBV-EVs also transfer LMP-1 to B cells and induce their proliferation and differentiation into a plasma cell-like phenotype, causing IgG overproduction and a higher risk of autoimmune disorders [114].Virus-EVs transporting host miRNA also enhance migration and proliferation of recipient cancer cells by inducing expression of proinflammatory cytokines that limit apoptosis [HIV [115].