Figure 12.
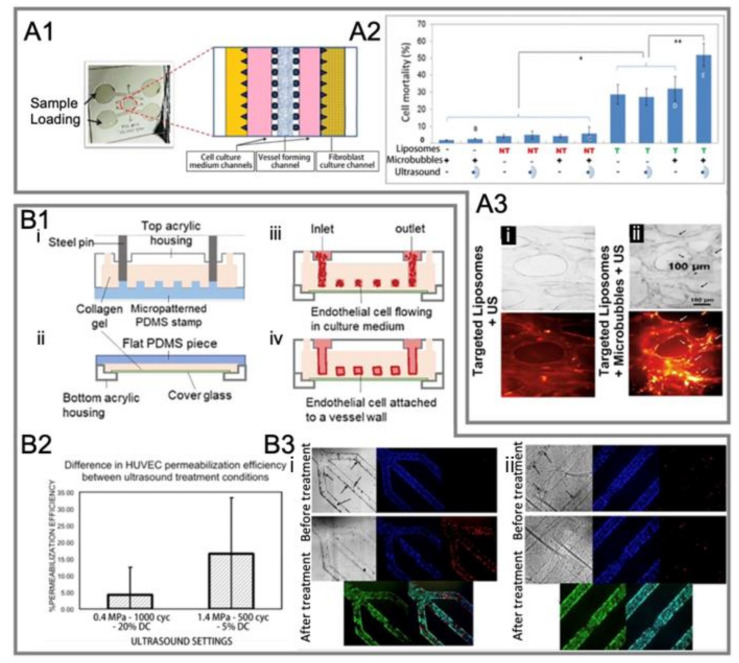
Another two representative studies on the ultrasound-mediated opening of vascular barriers in three-dimensional BOC. (A1) A microvascular chip comprises several channels partitioned by micro-posts [101]. (A2) Effect of different test conditions on cell mortality in the microvasculature [101]. (A3) Microbubbles increased the toxicity of DOX-loaded liposomes to cells under ultrasound exposure [101]. Microvessels were perfused with (i) integrin-targeted liposomes alone or (ii) integrin-targeted liposomes + microbubbles, then washed and treated with ultrasound. Bright field (top) and TRITC fluorescent (bottom) images were taken after 24 h. Black arrows in the bright-field image in panel (ii) show cells extruded from nearby vessels. White arrows in TRITC image in panel (ii) show liposomes that have penetrated the external vessel walls. (B1) A perusable in vitro model for the 3D culture of ECs [37]. (i,ii) Preparation of the microvascular network (MVN). (i) The top half of the MVN: liquid collagen I was injected into the space enclosed by a patterned PDMS stamp and a top acrylic housing. (ii) The bottom half of an MVN: a thin collagen layer was applied on top of a cover glass that sits above the window of a bottom acrylic housing. (iii) After combing the two MVN halves, HUVECs were introduced to the collagen scaffold. (iv) HUVECs attached to the collagen walls overnight and formed a vascular endothelium after 2–3 days of culture. (B2) Assessment of HUVEC permeabilization efficiency under different ultrasound treatment conditions [37]. (B3) Bright field and fluorescence images of the vascular barrier before and after ultrasound-microbubble treatment under acoustic conditions of (i) 1.4 MPa, 500 cycles, 5% duty cycles (DC) and (ii) 0.4 MPa, 1000 cycles, 20% DC. Hoechst (blue) stains HUVEC nuclei; PI (red) stains damaged plasma membranes of cells, which indicates sonoporation or cell death [37].