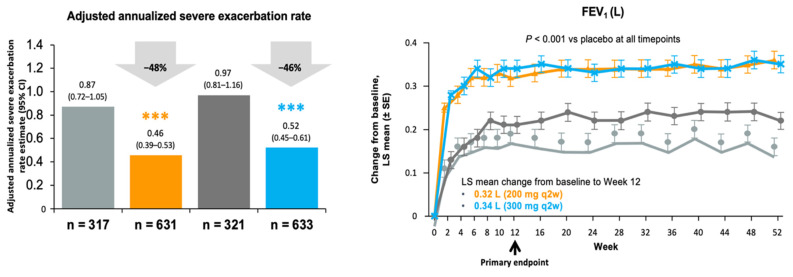
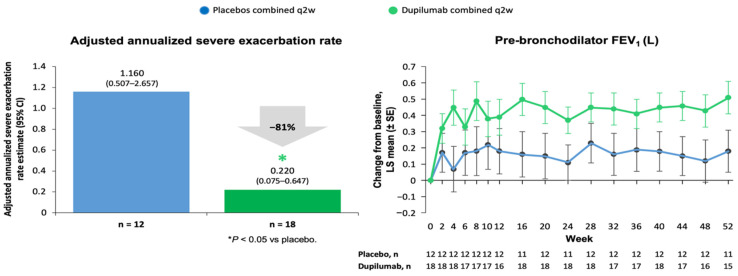
Figure 4.
Clinical outcomes of annualized severe asthma exacerbation rate (left panels) and change in lung function (right panels) in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled one-year pivotal trial of dupilumab in adult patients with moderate-severe asthma. Top panel: Results of overall study. Dupilumab reduced asthma exacerbations by 46–48% and improved lung function (*** p < 0.001) in both dosage arms of active treatment compared to placebo. Bottom panel: Post hoc analysis of study subjects with serologic ABPA (IgE > 1000 IU/mL, Af-specific IgE > 0.35 IU/mL, eosinophil count > 500) showing pooled results for actively treated subject arms compared to placebo. Dupilumab treatment reduced exacerbations and improved lung function to an even greater degree than seen in the overall study results. Adapted from references [80,82].