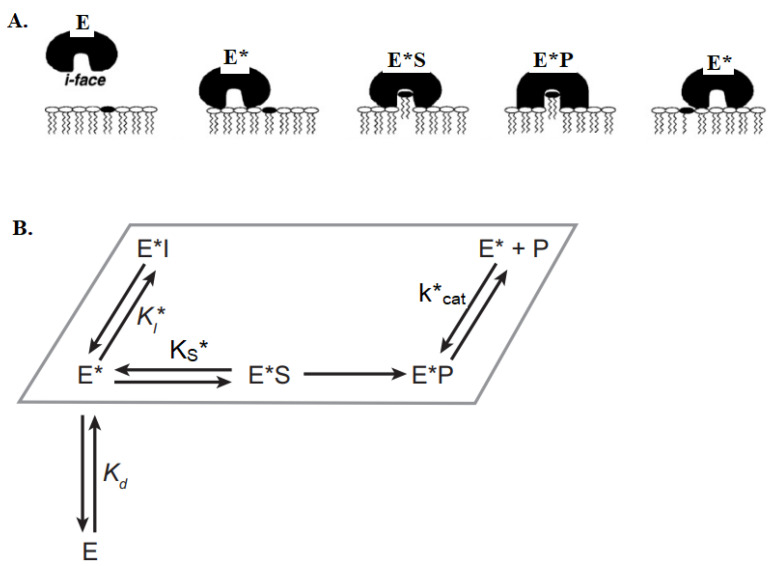
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of interfacial binding and catalytic action of sPLA2. (A) The binding of the sPLA2 at the lipid/water interface through the i-face is essential for catalysis. The enzyme passes along the horizontal plane on the bilayer, while hydrolyzing the phospholipid molecules and releasing the LPL and FA products [20]. (B) The minimal kinetic scheme for the catalytic cycle of sPLA2 is shown in a parallelogram box that represents the lipid bilayer. Here, E denotes enzyme in the aqueous phase, E* denotes enzyme in a membrane-bound state without substrate and Kd is the interfacial dissociation constant for the enzyme at the interface. KS, Kcat and KI are the dissociation constants for substrate, product and inhibitor, respectively. E*S and E*P denote the enzyme-bound substrate and enzyme-bound product, respectively. Adapted with permission from [20]. Copyright 2001, American Chemical Society.