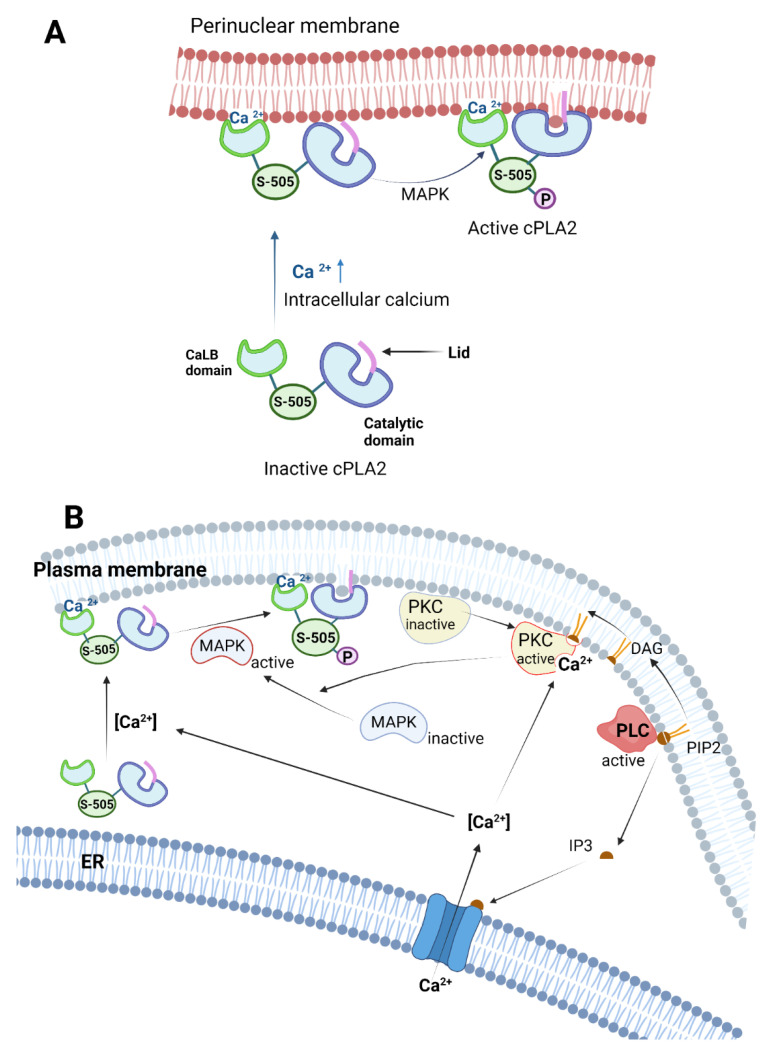
Figure 12.
Multiple activation pathways for cPLA2 via calcium, phosphorylation and secondary messengers. (A) Ca2+ ion helps in binding the CaLB domain of the cPLA2 with the membrane; however, the catalytic domain is not oriented in the right direction for hydrolyzing the phospholipid substrate. Phosphorylation in the flexible linker of the cPLA2 via MAPK induces optimal conformation of the catalytic domain, which facilitates partial penetration of the catalytic domain into the membrane. (B) The schematics for multiple regulation pathways for cPLA2. PIP2 is hydrolyzed by PLC to form secondary messengers such as IP3 and DAG. IP3 opens up the Ca2+ ion channel in the perinuclear membrane of the ER, which increases the intracellular Ca2+ concentration. The DAG and the Ca2+ simultaneously activates PKC, which subsequently activates MAPK. The activated MAPK phosphorylates the cPLA2, which further enhances the cPLA2 activity. Created with BioRender.com.